Page 62 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 62
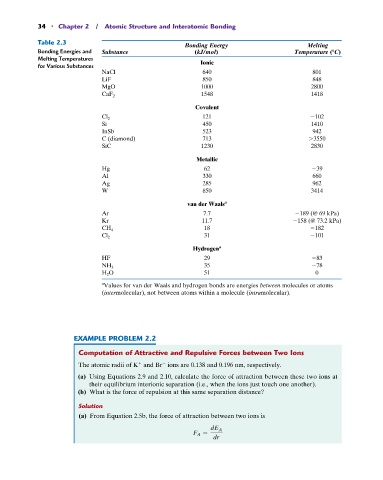
34 • Chapter 2 / Atomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding
Table 2.3
Bonding Energy Melting
Bonding Energies and Substance (kJ/mol) Temperature ( C)
Melting Temperatures
for Various Substances Ionic
NaCl 640 801
LiF 850 848
MgO 1000 2800
CaF 2 1548 1418
Covalent
Cl 2 121 102
Si 450 1410
InSb 523 942
C (diamond) 713 3550
SiC 1230 2830
Metallic
Hg 62 39
Al 330 660
Ag 285 962
W 850 3414
van der Waals a
Ar 7.7 189 (@ 69 kPa)
Kr 11.7 158 (@ 73.2 kPa)
CH 4 18 182
Cl 2 31 101
Hydrogen a
HF 29 83
NH 3 35 78
H 2 O 51 0
a Values for van der Waals and hydrogen bonds are energies between molecules or atoms
(intermolecular), not between atoms within a molecule (intramolecular).
EXAMPLE PROBLEM 2.2
Computation of Attractive and Repulsive Forces between Two Ions
The atomic radii of K and Br ions are 0.138 and 0.196 nm, respectively.
(a) Using Equations 2.9 and 2.10, calculate the force of attraction between these two ions at
their equilibrium interionic separation (i.e., when the ions just touch one another).
(b) What is the force of repulsion at this same separation distance?
Solution
(a) From Equation 2.5b, the force of attraction between two ions is
dE A
F A =
dr