Page 78 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 78
65
2.3. The Crystalline State
plane. Since we have a twofold rotation axis and two glide planes, the crystal system
is likely orthorhombic (Table 2.5 – defined by 3 twofold rotation axes/mirror
planes). To summarize, we would have a primitive orthorhombic unit cell, with a
c-glide ⊥ a, an a-glide ⊥ b, and a 2 1 screw axis // c. Hence, the space group symbol
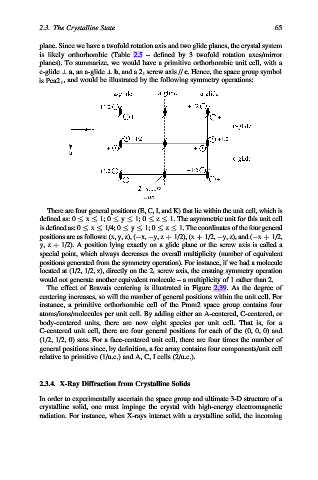
is Pca2 1 , and would be illustrated by the following symmetry operations:
There are four general positions (E, C, I, and K) that lie within the unit cell, which is
defined as: 0 x 1; 0 y 1; 0 z 1. The asymmetric unit for this unit cell
is defined as: 0 x 1/4; 0 y 1; 0 z 1. The coordinates of the four general
positions are as follows: (x, y, z), ( x, y, z þ 1/2), (x þ 1/2, y, z), and ( x þ 1/2,
y, z þ 1/2). A position lying exactly on a glide plane or the screw axis is called a
special point, which always decreases the overall multiplicity (number of equivalent
positions generated from the symmetry operation). For instance, if we had a molecule
located at (1/2, 1/2, z), directly on the 2 1 screw axis, the ensuing symmetry operation
would not generate another equivalent molecule – a multiplicity of 1 rather than 2.
The effect of Bravais centering is illustrated in Figure 2.39. As the degree of
centering increases, so will the number of general positions within the unit cell. For
instance, a primitive orthorhombic cell of the Pmm2 space group contains four
atoms/ions/molecules per unit cell. By adding either an A-centered, C-centered, or
body-centered units, there are now eight species per unit cell. That is, for a
C-centered unit cell, there are four general positions for each of the (0, 0, 0) and
(1/2, 1/2, 0) sets. For a face-centered unit cell, there are four times the number of
general positions since, by definition, a fcc array contains four components/unit cell
relative to primitive (1/u.c.) and A, C, I cells (2/u.c.).
2.3.4. X-Ray Diffraction from Crystalline Solids
In order to experimentally ascertain the space group and ultimate 3-D structure of a
crystalline solid, one must impinge the crystal with high-energy electromagnetic
radiation. For instance, when X-rays interact with a crystalline solid, the incoming