Page 259 - Mathematical Models and Algorithms for Power System Optimization
P. 259
Optimization Method for Load Frequency Feed Forward Control 251
disturbance is known), does not need to bear any the impact of disturbance, namely, it is
possible to find a control law to fully compensate the disturbance quantity and control the
frequency changes.
Thefollowingshowshowtoderivetheloadfrequencycontrollawaspertheinvarianceprinciple.
The estimation or forecasting values of load disturbance ΔP L are distributed to each unit by the
following equation:
ΔP Lj ¼ α j ΔP L
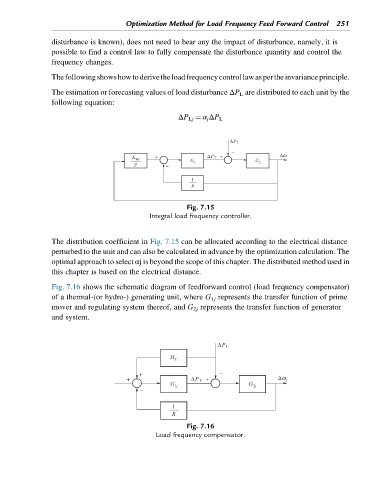
Fig. 7.15
Integral load frequency controller.
The distribution coefficient in Fig. 7.15 can be allocated according to the electrical distance
perturbed to the unit and can also be calculated in advance by the optimization calculation. The
optimal approach to select αj is beyond the scope of this chapter. The distributed method used in
this chapter is based on the electrical distance.
Fig. 7.16 shows the schematic diagram of feedforward control (load frequency compensator)
of a thermal-(or hydro-) generating unit, where G 1j represents the transfer function of prime
mover and regulating system thereof, and G 2j represents the transfer function of generator
and system.
Fig. 7.16
Load frequency compensator.