Page 75 - Mathematical Models and Algorithms for Power System Optimization
P. 75
Optimization of Annual Generator Maintenance Scheduling 65
To make the GMS procedure work for all the annual, quarterly, and monthly plans, a day should
be selected as the time unit of GMS calculation, which not only keeps the annually and
quarterly plans more flexible but also ensures the operability of monthly plans.
3.5.2 Introducing of Operation Index
The GMS’s ability should be evaluated before GMS calculation. The GMS ability is defined as
the difference between the installed system capacity and the equivalent load. The larger the
difference or reserve margin, the stronger the GMS ability. Thus, the concept of operation index
may be introduced to represent GMS ability of power systems.
The operation index is defined as follows:
N M
X
P Gi M Di
i¼1
OP index ¼ (3.18)
N T
X X
T P Gi P EL tðÞ
i¼1 i¼1
P EL tðÞ ¼ P L tðÞ P HY tðÞ P SG tðÞ P EP tðÞ + P SZ tðÞ (3.19)
where N M —total number of units involved in maintenance in the total study time interval,
M Di —number of maintenance duration of unit i, T—total time intervals to be studied,
P Gi —capacity (MW) of unit i, P EL (t)—system equivalent load (MW) in the time interval t.
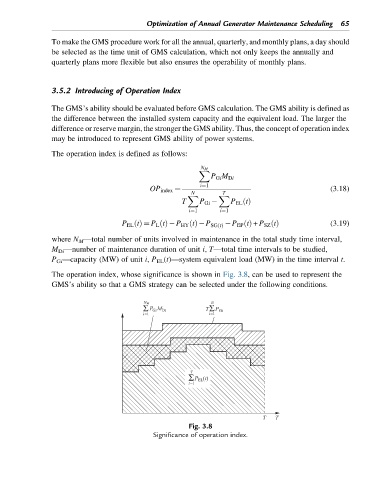
The operation index, whose significance is shown in Fig. 3.8, can be used to represent the
GMS’s ability so that a GMS strategy can be selected under the following conditions.
Fig. 3.8
Significance of operation index.