Page 114 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 114
THERMODYNAMICS AND HEAT TRANSFER 103
3.2.3 Specific heat relationships or, if the kinetic energy is small (which is usually the
case)
There are two particular values of specific heat: that at h, -hl =Q- W (neglecting height differences)
constant volume c,, and that at constant pressure cp.
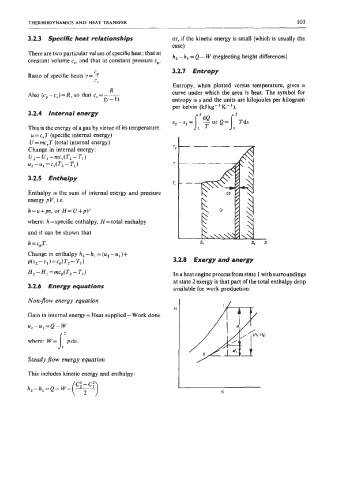
C 3.2.7 Entropy
Ratio of specific heats y = -1!
C"
Entropy, when plotted versus temperature, gives a
R curve under which the area is heat. The symbol for
Also (cp - c,) = R, so that c, = -
(Y-1) entropy is s and the units are kilojoules per kilogram
per kelvin (kJkg-'K-').
3.2.4 Internal energy
This is the energy of a gas by virtue of its temperature.
u =cVT (specific internal energy)
U =mc,T (total internal energy)
Change in internal energy:
U, - U, = mc,( T, - T,)
u2-u1=c,(T2-T1)
3.2.5 Enthalpy
Enthalpy is the sum of internal energy and pressure
energy pV, i.e.
h=u+pv, or H=U+pV
where: h = specific enthalpy, H = total enthalpy
and it can be shown that
h=c,T.
Change in enthalpy h,-h, =(u,-u,)+
Pb, - 01 1 = CJT, - Tl 1 3.2.8 Exergy and anergy
H, - H, =mc,(T, - TI) In a heat engine process from state 1 with surroundings
at state 2 exergy is that part of the total enthalpy drop
3.2.6 Energy equations available for work production.
Non-pow energy equation
Gain in internal energy =Heat supplied - Work done
uz-ul=Q- W
j12
where: W= pdv.
Steady pow energy equation
This includes kinetic energy and enthalpy:
I
S