Page 117 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 117
106 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
3.3 Vapours
A substance may exist as a solid, liquid, vapour or gas. rise (at constant pressure) required to do this is known
A mixture of liquid (usually in the form of very small as the ‘degree of superheat’. The method of determin-
drops) and dry vapour is known as a ‘wet vapour’. ing the properties of vapours is given, and is to be used
When all the liquid has just been converted to vapour in conjunction with vapour tables, the most compre-
the substance is referred to as ‘saturated vapour’ or hensive of which are for water vapour. Processes are
‘dry saturated vapour’. Further heating produces what shown on the temperature-entropy and en-
is known as ‘superheated vapour’ and the temperature thalpy-entropy diagrams.
Symbols used: Specific enthalpy of wet vapour
p=pressure (Nm-’ (=pascal); Nmm-2; bar h, = h, + x(h, - h,) = h, + xh,,
(E 1OSNm-’); millibar (E 100Nm-’)) specific entropy of wet vapour
t = temperature (“C)
t, = saturation temperature (“C) sx=sf+x(s,-sf)=sf +xs,,
T= absolute temperature (K N “C + 273) Superheated vapour Tables (e.g. for water) give
u = specific volume (m3 kg - ’) values of u, u, h, and s for a particular pressure and a
u,=specific volume of liquid (m3 kg-’) range of temperatures above the saturation tempera-
u,=specific volume of saturated vapour (m3 kg-’) ture t,. For steam above 70 bar use u=h-pu.
u = specific internal energy (kJ kg- I)
u, = specific internal energy of liquid (kJ kg- ’) 3.3.2 TemperatureEntropy diagram
ug= specific internal energy of vapour (kJ kg-’) (T-s diagram)
u,, = specific internal energy change from liquid to
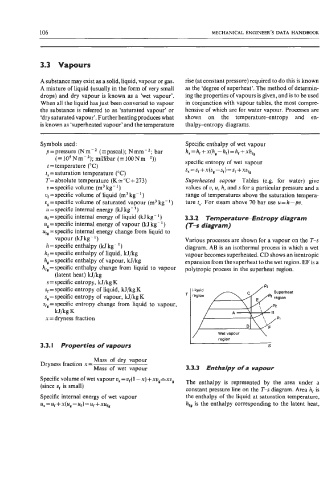
vapour (kJkg-’) Various processes are shown for a vapour on the T-s
h =specific enthalpy (kJ kg - I) diagram. AB is an isothermal process in which a wet
h, = specific enthalpy of liquid, kJ/kg vapour becomes superheated. CD shows an isentropic
h, = specific enthalpy of vapour, kJ/kg expansion from the superheat to the wet region. EF is a
h,, = specific enthalpy change from liquid to vapour polytropic process in the superheat region.
(latent heat) kJ/kg
s = specific entropy, kJ/kg K
sf = specific entropy of liquid, kJ/kg K reg m i
Liquid
Liquid
sg = specific entropy of vapour, kJ/kg K T region Fv
sfg = specific entropy change from liquid to vapour,
kJ/kg K
x = dryness fraction \ P1
/ Wet vapour \
region
3.3. I Properties of vapours S
Mass of dry vapour
Dryness fraction x =
Mass of wet vapour 3.3.3 Enthalpy of a vapour
Specific volume of wet vapour u, = uf( 1 - x) + XD,==XU, The enthalpy is represented by the area under a
(since u, is small) constant pressure line on the T-s diagram. Area h, is
Specific internal energy of wet vapour the enthalpy of the liquid at saturation temperature,
u, = Uf + x(u, - Uf) = Uf + XUfs h,, is the enthalpy corresponding to the latent heat,