Page 120 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 120
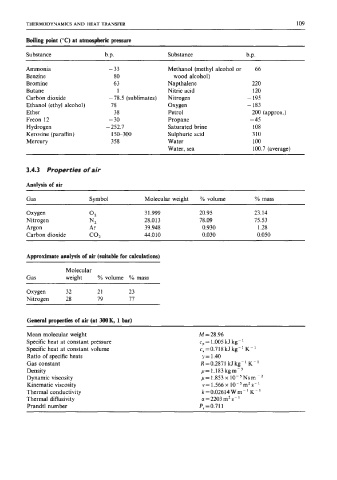
THERMODYNAMICS AND HEAT TRANSFER 109
Boiling point ("C) at atmospheric pressure
Substance b.p. Substance b.p.
Ammonia - 33 Methanol (methyl alcohol or 66
Benzine 80 wood alcohol)
Bromine 63 Napthalene 220
Butane 1 Nitric acid 120
Carbon dioxide - 78.5 (sublimates) Nitrogen - 195
Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) 78 Oxygen - 183
Ether 38 Petrol 200 (approx.)
Freon 12 - 30 Propane - 45
Hydrogen - 252.7 Saturated brine 108
Kerosine (paraffin) 150-300 Sulphuric acid 3 10
Mercury 358 Water 100
Water, sea 100.7 (average)
3.4.3 Properties of air
Analysis of air
Gas Symbol Molecular weight YO volume YO mass
Oxygen 02 3 1.999 20.95 23.14
Nitrogen NZ 28.013 78.09 75.53
Argon Ar 39.948 0.930 1.28
Carbon dioxide CO, 44.010 0.030 0.050
Approximate analysis of air (suitable for calculations)
Molecular
Gas weight % volume YO mass
Oxygen 32 21 23
Nitrogen 28 79 77
General properties of air (at 300K, 1 bar)
Mean molecular weight M = 28.96
Specific heat at constant pressure cP= 1.005 kJ kg-'
Specific heat at constant volume c,=0.718 kJ kg-' K-'
Ratio of specific heats y= 1.40
Gas constant R=0.2871 kJkg-'K-'
Density p= 1.183 kgm-3
Dynamic viscosity p=1.853x 10-5Nsm-Z
Kinematic viscosity v=1.566x 10-5m2s-1
Thermal conductivity k = 0.02614 W m- K- '
Thermal diffusivity a = 2203 m2 s-
Prandtl number P,=0.711