Page 208 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 208
196 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
Cutting fluid applications (continued)
Group Description Advantages
Straight oils Mineral or fatty oils (lard, sperm, Good lubricant. Often unstable.
olive, neat’s foot, rape, etc.) alone
or compounded
Sulphurized EP oils Straight oils with sulphur, zinc oxide Average coolant. Good lubricant.
or other additives (0.2-0.8%S) Pressure resistant. Prevents welding
of chip on tool
Sulphochlorinated EP oils Mineral and fatty oil blends with More efficient than sulphurized oils.
sulphur and chlorine additives For most arduous conditions.
Highly resistant to welding of chip
on tool
Chlorinated materials Carbon tetrachloride and Very good EP fluid. Highly
trichlorethylene alone or blended dangerous to use
with oils
Gases and vapours Air, oil mist, CO, Limited cooling power. Chip
dispersed
EP, extreme pressure.
5.8 Casting
Casting is the forming of metal or plastic parts by removing it from the mould. Further processing is
introducing the liquid material to a suitably shaped usually required.
cavity (mould), allowing it to solidify, and then
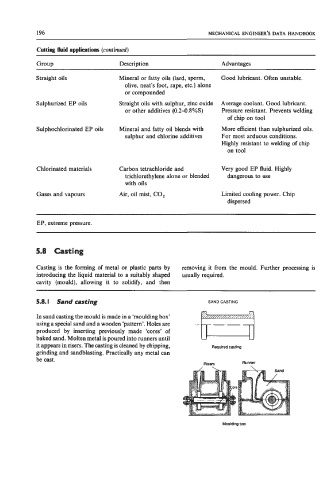
5.8.1 Sand casting SAND CASTING
In sand casting the mould is made in a ‘moulding box’
using a special sand and a wooden ‘pattern’. Holes are .-
produced by inserting previously made ‘cores’ of
baked sand. Molten metal is poured into runners until
it appears in risers. The casting is cleaned by chipping, Required casting
grinding and sandblasting. Practically any metal can
be cast.
Risers Runner
Moulding box