Page 58 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 58
STRENGTHS OF MATERIALS 47
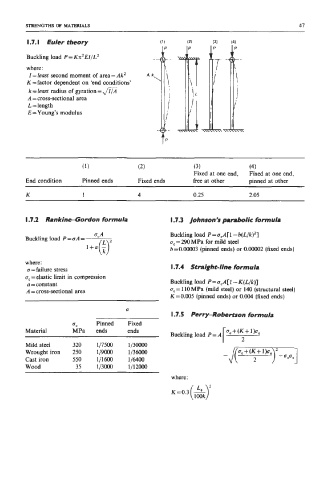
I .7. I Euler theory
Buckling load P=Kn2EIJL2
where:
I = least second moment of area = Ak2 A, k,
K = factor dependent on ‘end conditions’
k = least radius of gyration =
A = cross-sectional area
L = length
E =Young’s modulus
-4
1
(1) (2) (3) (4)
Fixed at one end, Fixed at one end,
End condition Pinned ends Fixed ends free at other pinned at other
K 1 4 0.25 2.05
I .7.2 Rankine-Gordon formula I .7.3 Johnson’s parabolic formula
OCA Buckling load P=a,ACl -b(L/k)21
Buckling load P = aA = a, = 290 MPa for mild steel
Ita(:)’ b=0.00003 (pinned ends) or O.ooOo2 (fixed ends)
where:
c = failure stress I .7.4 Straight-line formula
a, =elastic limit in compression
a =constant Buckling load P = a,A[ 1 - K(L/k)]
A =cross-sectional area a, = 110 MPa (mild steel) or 140 (structural steel)
K=0.005 (pinned ends) or 0.004 (fixed ends)
a
I .7.5 Perry-Robertson formula
DE Pinned Fixed
Material MPa ends ends
Buckling load P = A P+(:+l)ae
Mild steel 320 1/7500 1/3oooO
Wrought iron 250 1/9ooo 1/36000
Cast iron 550 1/1600 1/6400
wood 35 1/3000 1/12000
where:
K =0.3 (