Page 75 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 75
64 MECHANICAL ENGINEER'S DATA HANDBOOK
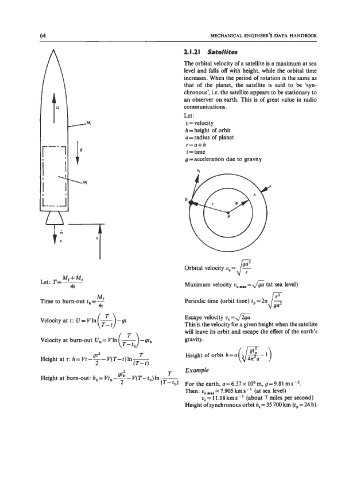
2. I .2 I Satellites
The orbital velocity of a satellite is a maximum at sea
level and falls off with height, while the orbital time
increases. When the period of rotation is the same as
that of the planet, the satellite is said to be 'syn-
chronous', i.e. the satellite appears to be stationary to
an observer on earth. This is of great value in radio
communications.
Let:
u = velocity
h = height of orbit
a = radius of planet
r=a+h
t = time
g = acceleration due to gravity
V.
S
Orbital velocity 0, =E
M,+M,
Let: T=-
m Maximum velocity u, m.l = & (at sea level)
M
Time to bum-out t, = f Periodic time (orbit time) t, = 2n 6
m
Velocity at t: U = Vln - Escape velocity ue=+
(TT_t)-gt This is the velocity for a given height when the satellite
will leave its orbit and escape the effect of the earth's
Velocity at burn-out U,= Vln - gravity.
( TTt,,)-gtb
9tZ T
Height at t: h= Vt--- V(T-t)ln- Height of orbit h=a (6-1)
2 (T-0
Example
gt: T
Height at burn-out: h,= Vt,--- V(T-t,)ln-
2 (T- tb) For the earth, a=6.37x 106m, g=9.81m~-~.
Then: u, ~x = 7.905 km s- ' (at sea level)
u,=ll.l8kms-' (about 7 miles per second)
Height of synchronous orbit h, = 35 700 km (tP = 24 h).