Page 317 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 317
308 Mathematical Models of Dynamic Physical Systems
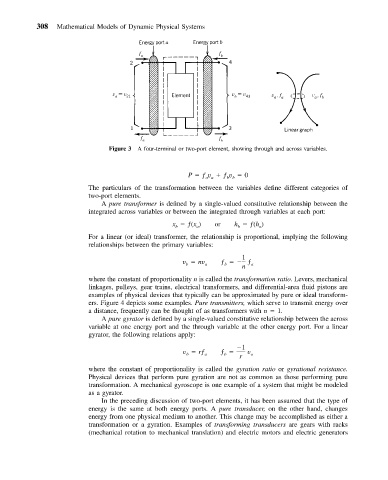
Figure 3 A four-terminal or two-port element, showing through and across variables.
P ƒ v ƒ v 0
aa
bb
The particulars of the transformation between the variables define different categories of
two-port elements.
A pure transformer is defined by a single-valued constitutive relationship between the
integrated across variables or between the integrated through variables at each port:
x ƒ(x ) or h ƒ(h )
a
b
a
b
For a linear (or ideal) transformer, the relationship is proportional, implying the following
relationships between the primary variables:
1
v nv a ƒ ƒ a
b
b
n
where the constant of proportionality n is called the transformation ratio. Levers, mechanical
linkages, pulleys, gear trains, electrical transformers, and differential-area fluid pistons are
examples of physical devices that typically can be approximated by pure or ideal transform-
ers. Figure 4 depicts some examples. Pure transmitters, which serve to transmit energy over
a distance, frequently can be thought of as transformers with n 1.
A pure gyrator is defined by a single-valued constitutive relationship between the across
variable at one energy port and the through variable at the other energy port. For a linear
gyrator, the following relations apply:
1
v rƒ a ƒ v a
b
b
r
where the constant of proportionality is called the gyration ratio or gyrational resistance.
Physical devices that perform pure gyration are not as common as those performing pure
transformation. A mechanical gyroscope is one example of a system that might be modeled
as a gyrator.
In the preceding discussion of two-port elements, it has been assumed that the type of
energy is the same at both energy ports. A pure transducer, on the other hand, changes
energy from one physical medium to another. This change may be accomplished as either a
transformation or a gyration. Examples of transforming transducers are gears with racks
(mechanical rotation to mechanical translation) and electric motors and electric generators