Page 201 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 201
190 Heat-Transfer Fundamentals
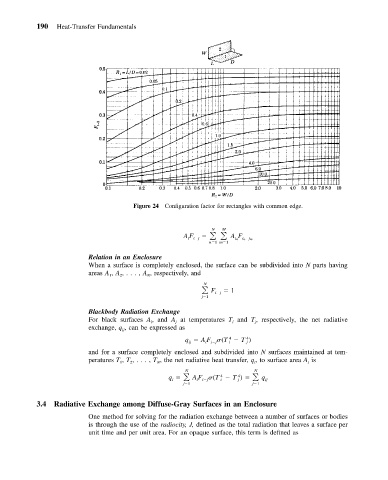
Figure 24 Configuration factor for rectangles with common edge.
N
M
AF AF
ii j i n i j m
n
n 1 m 1
Relation in an Enclosure
When a surface is completely enclosed, the surface can be subdivided into N parts having
areas A , A ,..., A , respectively, and
2
N
1
F 1
N
j 1 i j
Blackbody Radiation Exchange
For black surfaces A , and A at temperatures T and T , respectively, the net radiative
i j i j
exchange, q , can be expressed as
ij
4
4
q AF (T T )
ij i i j i j
and for a surface completely enclosed and subdivided into N surfaces maintained at tem-
peratures T , T , ..., T , the net radiative heat transfer, q , to surface area A is
1 2 N i i
q AF (T T ) q
N
N
4
4
i
j 1 i i j i j j 1 ij
3.4 Radiative Exchange among Diffuse-Gray Surfaces in an Enclosure
One method for solving for the radiation exchange between a number of surfaces or bodies
is through the use of the radiocity, J, defined as the total radiation that leaves a surface per
unit time and per unit area. For an opaque surface, this term is defined as