Page 512 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 512
5 Materials for Cryogenic Service 501
33
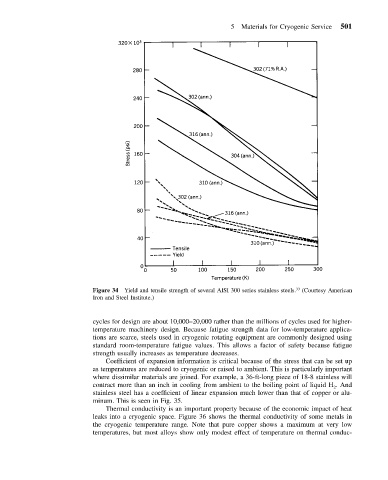
Figure 34 Yield and tensile strength of several AISI 300 series stainless steels. (Courtesy American
Iron and Steel Institute.)
cycles for design are about 10,000–20,000 rather than the millions of cycles used for higher-
temperature machinery design. Because fatigue strength data for low-temperature applica-
tions are scarce, steels used in cryogenic rotating equipment are commonly designed using
standard room-temperature fatigue values. This allows a factor of safety because fatigue
strength usually increases as temperature decreases.
Coefficient of expansion information is critical because of the stress that can be set up
as temperatures are reduced to cryogenic or raised to ambient. This is particularly important
where dissimilar materials are joined. For example, a 36-ft-long piece of 18-8 stainless will
contract more than an inch in cooling from ambient to the boiling point of liquid H . And
2
stainless steel has a coefficient of linear expansion much lower than that of copper or alu-
minum. This is seen in Fig. 35.
Thermal conductivity is an important property because of the economic impact of heat
leaks into a cryogenic space. Figure 36 shows the thermal conductivity of some metals in
the cryogenic temperature range. Note that pure copper shows a maximum at very low
temperatures, but most alloys show only modest effect of temperature on thermal conduc-