Page 517 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 517
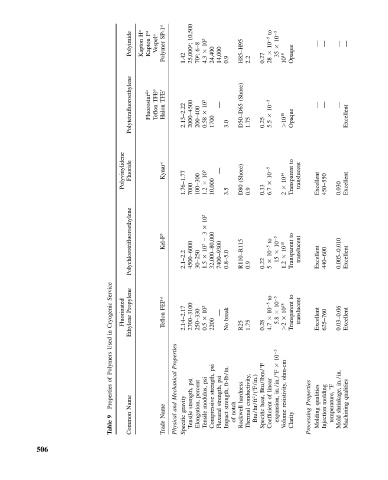
Polyimide H a Kapton F a Kapton Vespel a SP-1 a Polymer 1.42 10,500 25,000 g ; 6–8 70 g ; 10 5 4.3 24,400 14,000 0.9 H85–H95 2.2 0.27 to 10 5 28 10 5 35 10 18 Opaque — — — —
Polytetrafluoroethylene Fluorosint d,e TFE a Teflon TFE f Halon 2.13–2.22 2000–4500 200–400 10 5 0.58 1700 — 3.0 (Shore) D50–D65 1.75 0.25 10 5 5.5 10 18 Opaque — — — Excellent
Polyvinylidene Fluoride Kynar c 1.76–1.77 7000 100–300 10 5 1.2 10,000 — 3.5 (Shore) D80 0.9 0.33 10 5 6.7 10 14 2 to Transparent translucent Excellent 450–550 0.030 Excellent
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene Kel-F b 2.1–2.2 4500–6000 30–250 10 5 3 10 5 1.5 32,000–80,000 7400–9300 0.8–5.0 R110–R115 0.9 0.22 to 10 5 10 5 15 10 18 1.2 to Transparent translucent Excellent 440–600 0.005–0.010 Excellent
Service Propylene FEP a 5 to 10 5 to
Cryogenic Fluorinated Teflon 2.14–2.17 2700–3100 250–330 10 5 2200 — break 10 5 5.8 10 18 Transparent translucent Excellent 625–760 0.03–0.06 Excellent
in Ethylene 0.5 No R25 1.75 0.28 4.7 2
Used
Polymers Properties psi 10 5 ohm-cm
of Mechanical psi psi strength, psi ft-lb/in. Btu/lbm/ F linear in./in./ F F in./in.
Properties Name and gravity strength, percent modulus, strength, strength, hardness conductivity, Btu/hr/ft 2 /( F/in.) heat, of resistivity, Properties qualities molding shrinkage, qualities
9 Name Tensile Elongation, Tensile Compressive Flexural Impact notch of Rockwell Thermal Specific Coefficient expansion, Volume Clarity Processing Molding Injection temperature, Machining
Table Common Trade Physical Specific Mold
506