Page 521 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 521
510 Cryogenic Systems
Table 11 Properties of Cryogens Useful in Vapor Pressure Thermometers
Hydraulic
Triple Boiling Critical Heat at
Point Point Point dP/dT Boiling Point
2
Substance (K) (K) (K) (mm/K) (K/cm )
3 He — 3.19 3.32 790 0.000054
4 He — 4.215 5.20 715 0.00013
p-H 2 (20.4 K
equilibrium) 13.80 20.27 32.98 224 0.00023
Ne 24.54 27.09 44.40 230 0.0039
63.15 77.36 126.26 89 0.0067
N 2
Ar 83.81 87.30 150.70 80 0.013
54.35 90.18 154.80 79 0.011
O 2
At temperatures below 60 K, carbon resistors have been found to be convenient and
sensitive temperature sensors. Since the change in resistance per given temperature difference
is large (580 ohms/K would be typical at 4 K) the instrument range is small, and the resistor
must be selected and calibrated for use in the narrow temperature range required.
Germanium resistors that are single crystals of germanium doped with minute quantities
of impurities are also used throughout the cryogenic range. Their resistance varies approx-
imately logarithmically with temperature, but the shape of this relation depends on the
amount and type of dopant. Again, the germanium semiconductor must be selected and
calibrated for the desired service.
Thermistors, that is, mixed, multicrystal semiconductors, like carbon and germanium
resistors, give exponential resistance calibrations. They may be selected for order-of-
magnitude resistance changes over very short temperature ranges or for service over wide
temperature ranges. Calibration is necessary and may change with successive temperature
cycling. For this reason they should be temperature-cycled several times before use. These
sensors are cheap, extremely sensitive, easily read, and available in many forms. Thus they
are excellent indicators of modest accuracy but of high sensitivity, such as sensors for control
action. They do not, however, have the stability required for high accuracy.
6.2 Flow Measurement
Measurement of flow in cryogenic systems is often made difficult because of the need to
deal with a liquid at its boiling point. Thus any significant pressure drop causes vaporization,
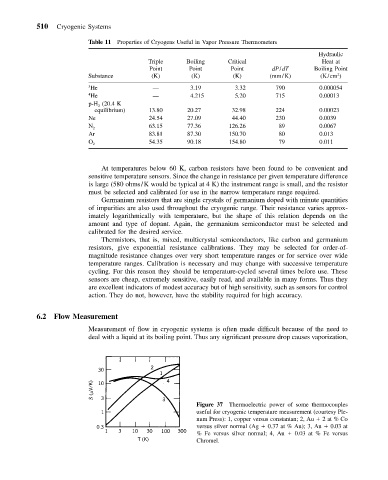
Figure 37 Thermoelectric power of some thermocouples
useful for cryogenic temperature measurement (courtesy Ple-
num Press): 1, copper versus constantan; 2, Au 2at % Co
versus silver normal (Ag 0.37 at % Au); 3, Au 0.03 at
% Fe versus silver normal; 4, Au 0.03 at % Fe versus
Chromel.