Page 111 - Singiresu S. Rao-Mechanical Vibrations in SI Units, Global Edition-Pearson (2017)
P. 111
108 Chapter 1 Fundamentals oF Vibration
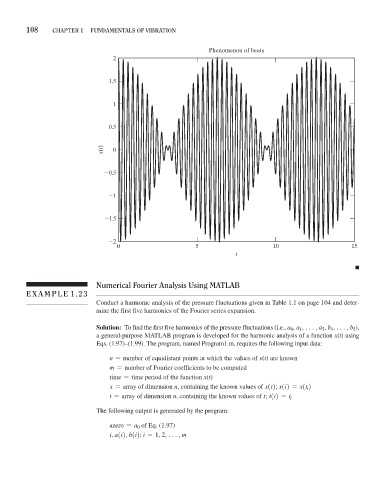
Phenomenon of beats
2
1.5
1
0.5
x(t) 0
0.5
1
1.5
2
0 5 10 15
t
■
numerical Fourier analysis using matlab
example 1.23
Conduct a harmonic analysis of the pressure fluctuations given in Table 1.1 on page 104 and deter-
mine the first five harmonics of the Fourier series expansion.
Solution: To find the first five harmonics of the pressure fluctuations (i.e., a 0 , a 1 , c, a 5 , b 1 , c, b 5 ),
a general-purpose MATLAB program is developed for the harmonic analysis of a function x(t) using
Eqs. (1.97)–(1.99). The program, named Program1.m, requires the following input data:
n = number of equidistant points at which the values of x(t) are known
m = number of Fourier coefficients to be computed
time = time period of the function x(t)
x = array of dimension n, containing the known values of x1t2; x1i2 = x1t i 2
t = array of dimension n, containing the known values of t; t1i2 = t i
The following output is generated by the program:
azero = a 0 of Eq. (1.97)
i, a1i2, b1i2; i = 1, 2, c, m