Page 199 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 199
184 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
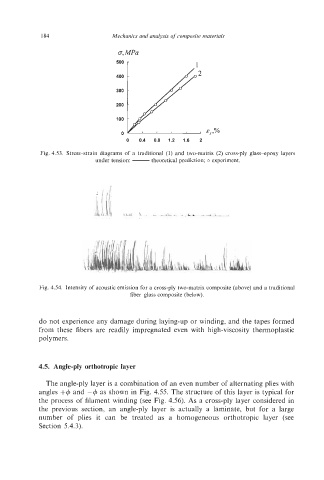
0, MPa
500
400
300
200
I00
E, ,%
0
0 0.4 0.8 1.2 1.6 2
Fig. 4.53. Stress-strain diagrams of a traditional (1) and two-matrix (2) cross-ply glass-epoxy layers
under tension: - theoretical prediction; o experiment.
Fig. 4.54. Intensity of acoustic emission for a cross-ply two-matrix composite (above) and a traditional
fiber-glass composite (below).
do not experience any damage during laying-up or winding, and the tapes formed
from these fibers are readily impregnated even with high-viscosity thermoplastic
polymers.
4.5. Angle-ply orthotropic layer
The angle-ply layer is a combination of an even number of alternating plies with
angles +4 and -4 as shown in Fig. 4.55. The structure of this layer is typical for
the process of filament winding (see Fig. 4.56). As a cross-ply layer considered in
the previous section, an angle-ply layer is actually a laminate, but for a large
number of plies it can be treated as a homogeneous orthotropic layer (see
Section 5.4.3).