Page 21 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 21
6 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
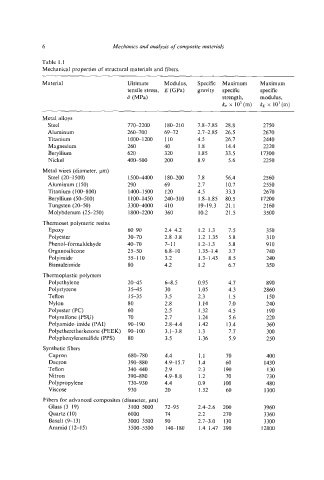
Table 1.1
Mechanical properties of structural materials and fibers.
Material Ultimate Modulus, Specific Maximum Maximum
tensile stress, E ((;Pa) gravity specific specific
if (MPa) strength, modulus,
ko x 10’ (m) kE x 10%(m)
Metal alloys
Steel 770-2200 18&210 7.8-7.85 28.8 2750
Aluminum 260-700 69-72 2.7-2.85 26.5 2670
Titanium 1000-1200 110 4.5 26.7 2440
Magnesium 260 40 1.8 14.4 2220
Beryllium 620 320 1.85 33.5 17300
Nickel 400-500 200 8.9 5.6 2250
Metal wires (diameter, pm)
Steel (20-1500) 150M400 180-200 7.8 56.4 2560
Aluminum (150) 290 69 2.7 10.7 2550
Titanium (I 00-800) 1400-1500 I20 4.5 33.3 2670
Beryllium (50-500) 1100-1450 240-310 1.8-1.85 80.5 17200
Tungsten (20-50) 3300-4000 410 19-19.3 21.1 2160
Molybdenum (25-250) 1800-2200 360 10.2 21.5 3500
Thermoset polymeric resins
EPOXY 6&90 2.4-4.2 1.2-1.3 7.5 350
Polyester 30-70 2.8-3.8 1.2-1.35 5.8 3IO
Phenol-formaldeh yde 40-70 7-11 1.2-1.3 5.8 910
Organosilicone 25-50 6.&10 1.35-1.4 3.7 740
Polyimide 55-110 3.2 1.3-1.43 8.5 240
Bismaleimide 80 4.2 1.2 6.7 350
Thermoplastic polymers
Polyethylene 20-45 6-8.5 0.95 4.7 890
Polystyrene 3545 30 1.05 4.3 2860
Teflon 15-35 3.5 2.3 1.5 150
Nylon 80 2.8 1.14 7.0 240
Polyester (PC) 60 2.5 1.32 4.5 190
Polysulfone (PSU) 70 2.7 1.24 5.6 220
Polyamide-imide (PAI) 90-190 2.84.4 I .42 13.4 360
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) 9&100 3.1-3.8 1.3 7.7 300
Polyphenylenesulfide (PPS) 80 3.5 1.36 5.9 250
Synthetic fibers
Capron 680-780 4.4 1.1 70 400
Dacron 390-880 4.915.7 1.4 60 1430
Teflon 3MO 2.9 2.3 190 130
Nitron 390-880 4.9-8.8 1.2 70 730
Polypropylene 730-930 4.4 0.9 IO0 480
Viscose 930 20 1.52 60 1300
Fibers for advanced composites (diameter, pm)
Glass (3-19) 3100-5000 72-95 2.4-2.6 200 3960
Quartz (10) 6000 74 2.2 270 3360
Basalt (9-13) 3000-3500 90 2.7-3.0 130 3300
Aramid (12-15) 3500-5500 140-180 1.4-1.47 390 12800