Page 237 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 237
222 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
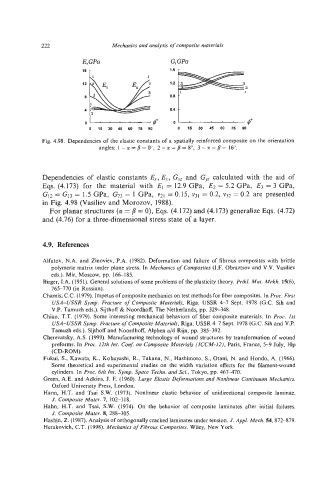
E,GPa G,GPa
1
128 2 6 b
3 0.8
1
4 0.4
oL------q9 o - &
0 15 30 45 60 75 90 0 16 30 45 60 75 90
Fig. 4.98. Dependencies of the elastic constants of a spatially reinforced composite on the orientation
angles: 1 - GL = fl = 0", 2 - a = p = 8", 3 - ct = fl = 16".
Dependencies of elastic constants E,, E,, GXzand G, calculated with the aid of
Eqs. (4.173) for the material with El = 12.9 GPa, E2 = 5.2 GPa, E3 = 3 GPa,
G12 = G13 = 1.5 GPa, G23 = 1 GPa, v21 = 0.15, ~31= 0.2, v32 = 0.2 are presented
in Fig. 4.98 (Vasiliev and Morozov, 1988).
For planar structures (a= /I= 0), Eqs. (4.172) and (4.173) generalize Eqs. (4.72)
and (4.76) for a three-dimensional stress state of a layer.
4.9. References
Alfutov, N.A. and Zinoviev, P.A. (1982). Deformation and failure of fibrous composites with brittle
polymeric matrix under plane stress. In Mechanics of Composites (I.F. Obraztsov and V.V. Vasiliev
eds.). Mir, Moscow, pp. 166-185.
Birger, LA. (1951). General solutions of some problems of the plasticity theory. Prikl. Mat. M&h. 15(6),
76S770 (in Russian).
Chamis, C.C. (1979). Impetus of composite mechanics on test methods for fiber composites. In Proc. First
USA-USSR Symp. Fracture of Composite Materials, Riga, USSR 4-7 Sept. 1978 (G.C. Sih and
V.P. Tamuzh eds.). Sijthoff & Noordhoff, The Netherlands, pp. 329-348.
Chiao, T.T. (1979). Some interesting mechanical behaviors of fiber composite materials. In Proc. 1st
USA-USSR Symp. Fracture of Composite Materials, Riga, USSR 4-7 Sept. 1978 (G.C. Sih and V.P.
Tamuzh eds.). Sijthoff and Noordhoff, Alphen a/d Rijn, pp. 385-392.
Cherevatsky, AS. (1999). Manufacturing technology of wound structures by transformation of wound
preforms. In Proc. 12th Int. Con$ on Composite Materials (ICCM-l2), Paris, France, 5-9 July, lop
(CD-ROM).
Fukui, S., Kawata, K., Kobayashi, R.,Takana, N., Hashimoto, S., Otani, N. and Hondo, A. (1966).
Some theoretical and experimental studies on the width variation effects for the filament-wound
cylinders. In Proc. 6fhInt. Symp. Space Techn. and Sci., Tokyo, pp. 467470.
Green, A.E. and Adkins, J. E. (1960). Large Elastic Deformations and Nonlinear Continuum Mechanics.
Oxford University Press, London.
Hann, H.T. and Tsai S.W. (1973). Nonlinear elastic behavior of unidirectional composite laminae.
J. Composite Mater. 7, 102-118.
Hahn, H.T. and Tsai, S.W. (1974). On the behavior of composite laminates after initial failures.
J. Composite Mater. 8, 288-305.
Hashin, Z. (1987). Analysis of orthogonally cracked laminates under tension. J. Appl. Mech. 54,872-879.
Herakovich, C.T. (1998). Mechanics of Fibrous Composites. Wiley, New York.