Page 317 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 317
302 Mechanics and analysis of composite muterials
7.1.I, Thernial conductivity
Heat flow through the unit area of the surface with normal n is linked with the
temperature gradient in the n-direction by Fourier's law as
where I is the thermal conductivity of the material. Temperature distribution along
the n-axis is governed by the following equation:
in which c and p are specific heat and density of the material and t is time. For a
steady (time-independent) temperature distribution, aT/at = 0 and Eq. (7.2) yields
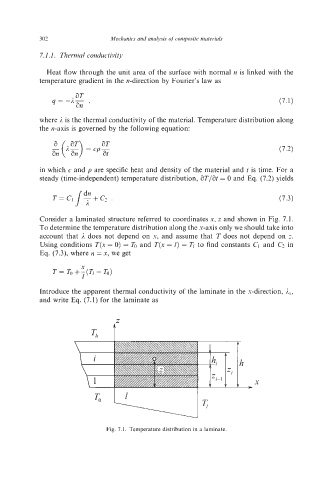
Consider a laminated structure referred to coordinates x,z and shown in Fig. 7.1.
To determine the temperature distribution along the x-axis only we should take into
account that 2 does not depend on x,and assume that T does not depend on z.
Using conditions T(x = 0) = TOand T(x = 1) = to find constants C1 and C? in
Eq. (7.3), where n =x,we get
'X
T = TO+- (T/ - To)
1
Introduce the apparent thermal conductivity of the laminate in the ..;-direction, 3,,
and write Eq. (7.1) for the laminate as
Z
Fig. 7.1. Temperature distribution in a laminate.