Page 34 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 34
Chapter 1. Introduction 19
lr v
1
oa - 2
0.6 -
0.4
0.4 - -
0.2 - -
0.2
0
0 40 80 120 160 200
1-
08 .
0.6 .
0.4 .
0.2 .
4
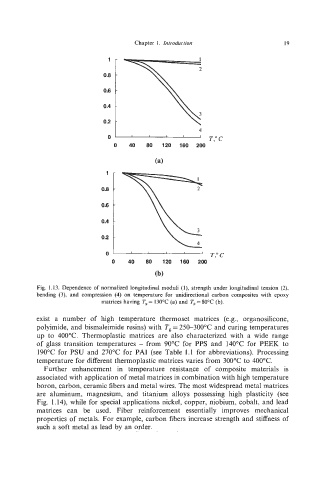
Fig. 1.13. Dependence of normalized longitudinal moduli (I), strength under longitudinal tension (2),
bending (3), and compression (4) on temperature for unidirectional carbon composites with epoxy
matrices having Tg= 130°C (a) and T, =80°C (b).
exist a number of high temperature thermoset matrices (e.g., organosilicone,
polyimide, and bismaleimide resins) with Tg=250-300°C and curing temperatures
up to 400°C. Thermoplastic matrices are also characterized with a wide range
of glass transition temperatures - from 90°C for PPS and 140°C for PEEK to
190°C for PSU and 270°C for PA1 (see Table 1.1 for abbreviations). Processing
temperature for different thermoplastic matrices varies from 300°C to 400°C.
Further enhancement in temperature resistance of composite materials is
associated with application of metal matrices in combination with high temperature
boron, carbon, ceramic fibers and metal wires. The most widespread metal matrices
are aluminum, magnesium, and titanium alloys possessing high plasticity (see
Fig. 1.14), while for special applications nickel, copper, niobium, cobalt, and lead
matrices can be used. Fiber reinforcement essentially improves mechanical
properties of metals. For example, carbon fibers increase strength and stiffness of
such a soft metal as lead by an order.