Page 369 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 369
354 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
where f = m/l. Substitution into Eqs. (7.70) and (7.71) and integration yield
(Tarnopol’skii and Roze, 1969)
where L = (1 +f2)3”.Simplifying this result under the assumption that f2 << 1 we
arrive at
E:) = ~ El . (7.72)
1 +g$
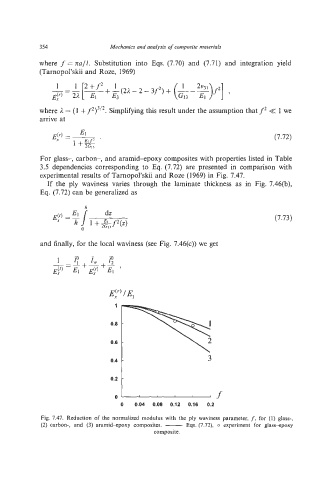
For glass-, carbon-, and aramid-poxy composites with properties listed in Table
3.5 dependencies corresponding to Eq. (7.72) are presented in comparison with
experimental results of Tarnopol’skii and Roze (1969) in Fig. 7.47.
If the ply waviness varies through the laminate thickness as in Fig. 7.46(b),
Eq. (7.72) can be generalized as
h
dz
(7.73)
0
and finally, for the local waviness (see Fig. 7.46(c)) we get
3
0.4
0.2
0
0 0.04 0.08 0.12 0.16 0.2
Fig. 7.47. Reduction of the normalized modulus with the ply waviness parameter, f. for (1) glass-,
(2) carbon-, and (3) aramid*poxy composites. -Eqs. (7.72), o experiment for glass-epoxy
composite.