Page 370 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 370
Chapter 7. Environmental, special loading, and manufacturing ejiec~s 355
where
and Et’ is specified by Eq. (7.73).
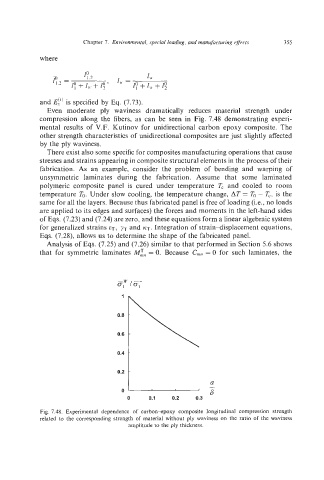
Even moderate ply waviness dramatically reduces material strength under
compression along the fibers, as can be seen in Fig. 7.48 demonstrating experi-
mental results of V.F. Kutinov for unidirectional carbon-epoxy composite. The
other strength characteristics of unidirectional composites are just slightly affected
by the ply waviness.
There exist also some specific for composites manufacturing operations that cause
stresses and strains appearing in composite structural elements in the process of their
fabrication. As an example, consider the problem of bending and warping of
unsymmetric laminates during the fabrication. Assume that some laminated
polymeric composite panel is cured under temperature T, and cooled to room
temperature To. Under slow cooling, the temperature change, AT = TO- T,, is the
same for all the layers. Because thus fabricated panel is free of loading (Le., no loads
are applied to its edges and surfaces) the forces and moments in the left-hand sides
of Eqs. (7.23) and (7.24) are zero, and these equations form a linear algebraic system
for generalized strains ET, yT and KT. Integration of strain-displacement equations,
Eqs. (7.28), allows us to determine the shape of the fabricated panel.
Analysis of Eqs. (7.25) and (7.26) similar to that performed in Section 5.6 shows
that for symmetric laminates M:,, = 0. Because C,,, = 0 for such laminates, the
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3
Fig. 7.48. Experimental dependence of carbon-epoxy composite longitudinal compression strength
related to the corresponding strength of material without ply waviness on the ratio of the waviness
amplitude to the ply thickness.