Page 381 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 381
366 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
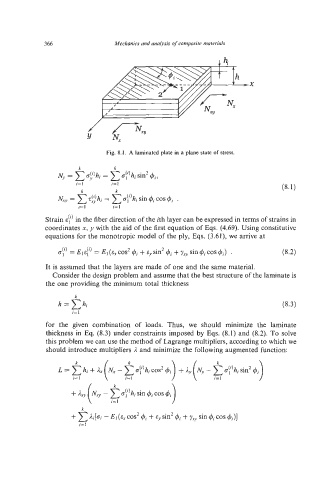
Fig. 8.1. A laminated plate in a plane state of stress.
Strain E? in the fiber direction of the ith layer can be expressed in terms of strains in
coordinates x,y with the aid of the first equation of Eqs. (4.69). Using constitutive
equations for the monotropic model of the ply, Eqs. (3.61), we arrive at
a? = EI $) = EI (Ex cos24i + cy sin24i + yxy sin 4;cos bi) . (8.2)
It is assumed that the layers are made of one and the same material.
Consider the design problem and assume that the best structure of the laminate is
the one providing the minimum total thickness
k
h=xhi (8.3)
i= I
for the given combination of loads. Thus, we should minimize the laminate
thickness in Eq. (8.3) under constraints imposed by Eqs. (8.1) and (8.2). To solve
this problem we can use the method of Lagrange multipliers, according to which we
should introduce multipliers A and minimize the following augmented function:
k k k
- aj')hi cos24;
i= I i= 1
k
+Ax? (IVr,, - af'h; sin 4;cos 4i
i= I