Page 453 - Mechanics of Asphalt Microstructure and Micromechanics
P. 453
Multiscale Modeling and Moisture Damage 445
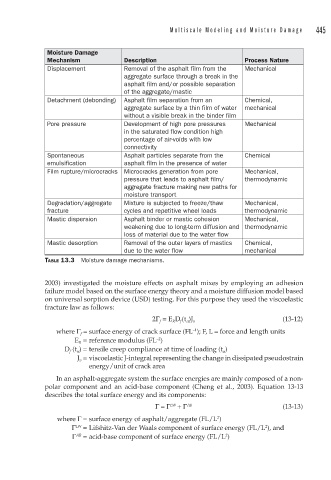
Moisture Damage
Mechanism Description Process Nature
Displacement Removal of the asphalt film from the Mechanical
aggregate surface through a break in the
asphalt film and/or possible separation
of the aggregate/mastic
Detachment (debonding) Asphalt film separation from an Chemical,
aggregate surface by a thin film of water mechanical
without a visible break in the binder film
Pore pressure Development of high pore pressures Mechanical
in the saturated flow condition high
percentage of air-voids with low
connectivity
Spontaneous Asphalt particles separate from the Chemical
emulsification asphalt film in the presence of water
Film rupture/microcracks Microcracks generation from pore Mechanical,
pressure that leads to asphalt film/ thermodynamic
aggregate fracture making new paths for
moisture transport
Degradation/aggregate Mixture is subjected to freeze/thaw Mechanical,
fracture cycles and repetitive wheel loads thermodynamic
Mastic dispersion Asphalt binder or mastic cohesion Mechanical,
weakening due to long-term diffusion and thermodynamic
loss of material due to the water flow
Mastic desorption Removal of the outer layers of mastics Chemical,
due to the water flow mechanical
TABLE 13.3 Moisture damage mechanisms.
2003) investigated the moisture effects on asphalt mixes by employing an adhesion
failure model based on the surface energy theory and a moisture diffusion model based
on universal sorption device (USD) testing. For this purpose they used the viscoelastic
fracture law as follows:
(13-12)
2Γ f = E R D f (t a )J v
where Γ f = surface energy of crack surface (FL ); F, L = force and length units
–1
–2
E R = reference modulus (FL )
D f (t a ) = tensile creep compliance at time of loading (t a )
J v = viscoelastic J-integral representing the change in dissipated pseudostrain
energy/unit of crack area
In an asphalt-aggregate system the surface energies are mainly composed of a non-
polar component and an acid-base component (Cheng et al., 2003). Equation 13-13
describes the total surface energy and its components:
Γ = Γ + Γ AB (13-13)
LW
2
where Γ = surface energy of asphalt/aggregate (FL/L )
2
Γ = Lifshitz-Van der Waals component of surface energy (FL/L ), and
LW
Γ = acid-base component of surface energy (FL/L )
AB
2