Page 87 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 87
76 SOME FUNDAMENTALS PHYSICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
OF
Table 2.6 (Continued)
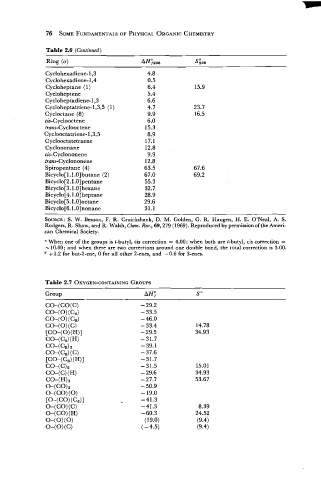
Ring (a) Aff"fzae S&8
Cyclohexadicne-1,3 4.8
Cyclohexadiene-1,4 0.5
Cycloheptane (1) 6.4 15.9
Cycloheptene 5.4
Cycloheptadiene-1,3 6.6
Cycloheptatriene- 1,3,5 (1) 4.7 23.7
Cycloctane (8) 9.9 16.5
cis-Cyclooctene 6.0
trans-Cyclooctene 15.3
Cyclooctatriene- l,3,5 8.9
Cyclooctatetraene 17.1
Cyclononane 12.8
cis-Cy clononene 9.9
trans-Cyclononene 12.8
Spiropentane (4) 63.5
Bicyclo[l .I .O]butane (2) 67.0
Bicyclo[2.1.0]pentane 55.3
Bicyclo[3.l.O]hexane 32.7
Bicyclo[4.1 .O]heptane 28.9
Bicyclo[5.1 .O]octane 29.6
Bicyclo[6. I .O]nonane 31.1
SOURCE: S. W. Benson, F. R. Cruickshank, D. M. Golden, G. R. Haugen, H. E. O'Neal, A. S.
Rodgers, R. Shaw, and R. Walsh, Chem. Rev., 69,279 (1969). Reproduced by permissionof the Ameri-
can Chemical Society.
"When one of the groups is t-butyl, cis correction = 4.00; when both are t-butyl, cis correction =
- 10.00; and when there are two corrections around one double bond, the total correction is 3.00.
* + 1.2 for but-2-ene, 0 for all other 2-enes, and -0.6 for 3-enes.
Table 2.7 OXYGEN-CONTAINING GROUPS
Group AH; So