Page 85 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 85
The experimental value is +4.54 kcal mole-l.
Note again, C-(H),(C,) is assumed to be equal to C-(H),(C).
Cycloalkanes
Correction factors must be applied for ring strain. These are given in Table 2.6.
Contributions to AH; due to gauche interactions between substituents and be-
tween substituent and ring must also be taken into account. (Contributions from
ring-ring gauche interactions are included in the ring strain.) Thus, for example,
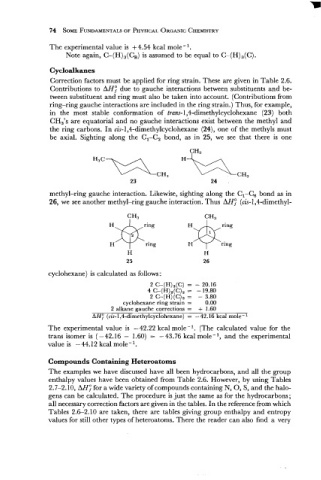
in the most stable conformation of tram- l,4-dimethylcyclohexane (23) both
CH,'s are equatorial and no gauche interactions exist between the methyl and
the ring carbons. In cis-l,4-dimethylcyclohexane (24), one of the methyls must
be axial. Sighting along the Cl-C, bond, as in 25, we see that there is one
methyl-ring gauche interaction. Likewise, sighting along the Cl-C, bond as in
26, we see another methyl-ring gauche interaction. Thus AH; (cis-1,4-dimethyl-
I@
H ring
H ring ring
cyclohexane) is calculated as follows
2 C-(H),(C) = - 20.16
4 C-(H),(C), = - 19.80
2 C-(II)(C)3 = - 3.80
cyclohexane ring strain = 0.00
2 alkane gauche corrections = + 1.60
AH; (cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane) = - 42.16 kcal mole- l
The experimental value is -42.22 kcal mole-l. (The calculated value for the
trans isomer is ( - 42.16 - 1.60) = - 43.76 kcal mole- l, and the experimental
value is - 44.12 kcal mole- l.
Compounds Containing Heteroatoms
The examples we have discussed have all been hydrocarbons, and all the group
enthalpy values have been obtained from Table 2.6. However, by using Tables
2.7-2.10, AH; for a wide variety of compounds containing N, 0, S, and the halo-
gens can be calculated. The procedure is just the same as for the hydrocarbons;
all necessary correction factors are given in the tables. In the reference from which
Tables 2.6-2.10 are taken, there are tables giving group enthalpy and entropy
values for still other types of heteroatoms. There the reader can also find a very