Page 80 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 80
Linear Free-Energy Relationships 69
-
pK or log k
i-
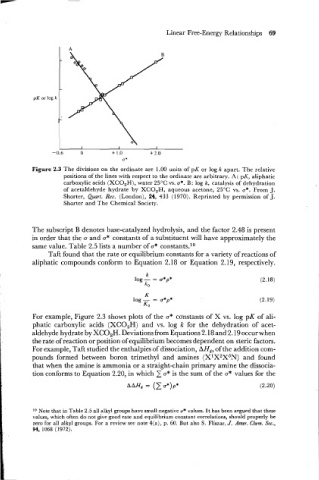
Figure 2.3 The divisions on the ordinate are 1.00 units of pK or log k apart. The relative
positions of the lines with respect to the ordinate are arbitrary. A: pK, aliphatic
carboxylic acids (XCO,H), water 25°C vs. o*. B: log k, catalysis of dehydration
of acetaldehyde hydrate by XCO,H, aqueous acetone, 25°C vs. a*. From J.
Shorter, Quart. Reu. (London), 24, 433 (1970). Reprinted by permission of J.
Shorter and The Chemical Society.
The subscript B denotes base-catalyzed hydrolysis, and the factor 2.48 is present
in order that the a and o* constants of a substituent will have approximately the
same value. Table 2.5 lists a number of o* constants.lg
Taft found that the rate or equilibrium constants for a variety of reactions of
aliphatic compounds conform to Equation 2.18 or Equation 2.19, respectively.
k
log - = o*p*
ko
K
log - = o*p*
KO
For example, Figure 2.3 shows plots of the a* constants of X vs. log pK of ali-
phatic carboxylic acids (XC02H) and vs. log k for the dehydration of acet-
aldehyde hydrate by XC02H. Deviations from Equations 2.18 and 2.19 occurwhen
the rate of reaction or position of equilibrium becomes dependent on steric factors.
For example, Taft studied the enthalpies of dissociation, AH,, of the addition com-
pounds formed between boron trimethyl and amines (X1X2X3N) and found
that when the amine is ammonia or a straight-chain primary amine the dissocia-
tion conforms to Equation 2.20, in which 2 o* is the sum of the o* values for the
l9 Note that in Table 2.5 all alkyl groups have small negative u* values. It has been argued that these
values, which often do not give good rate and equilibrium constant correlations, should properly be
zero for all alkyl groups. For a review see note 4(a), p. 60. But also S. Fliszar, J. Amer. Chem. Soc.,
94, 1068 (1972).