Page 174 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 174
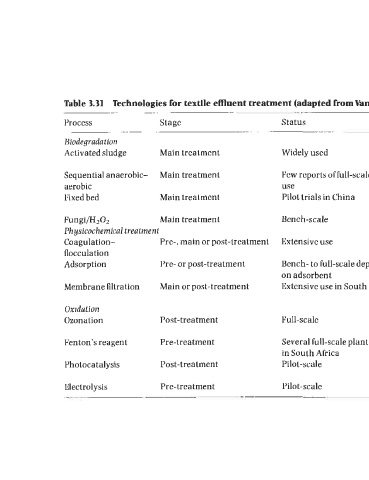
Table 3.31 Technologies for textile effluent treatment (adapted from Wndevivere et al., 1998)
-
Process Stage Status Performance Limitations
Biodegradation
Activated sludge Main treatment Widely used Bulk COD removal: partial High residual COD. ammonia,
nitrification colour
Sequential anaerobic- Main treatment Few reports of full-scale Better COD and colour High residual COD, colour
aerobic use removal than AS alone
Fixed bed Main treatment Pilot trials in China Better COD and colour Some residual colour
removal than AS
Fungi/H202 Main treatment Bench-scale Full decolourisation
Physicochemical treatment
Coagulation- Pre-, main or post-treatment Extensive use Almost full decolourisation; Unreliable performance: sludge
flocculation water reuse disposal
Adsorption Pre- or post-treatment Bench- to full-scale depending Water reuse with newer Sludge disposal or adsorbent
on adsorbent adsorbents regeneration
Membrane filtration Main or post-treatment Extensive use in South Africa Reliable performance; water Concentrate management
reuse
Oxidation
Ozonation Post-treatment Full-scale Full decolourisation: water Expensive: aldehydes formed
reuse
Fenton’s reagent Pre-treatment Several full-scale plant Full decolourisation
in South Africa
Photocatalysis Post-treatment Pilot-scale Near complete colour For final polishing only J
a
removal H
Electrolysis Pre-treatment Pilot-scale Full decolourisation Foaming: limited electrode life 2.
El