Page 245 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 245
Other Methods 227
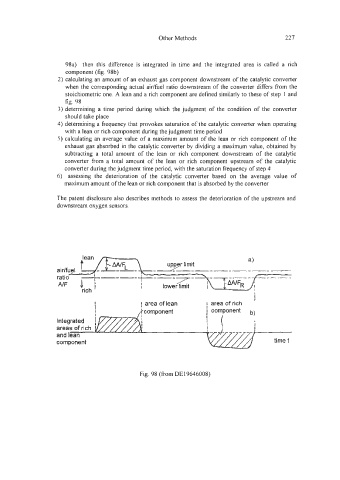
98a) then this difference is integrated in time and the integrated area is called a rich
component (fig. 98b)
2) calculating an amount of an exhaust gas component downstream of the catalytic converter
when the corresponding actual aidfuel ratio downstream of the converter differs from the
stoichiometric one. A lean and a rich component are defined similarly to these of step 1 and
fig. 98
3) determining a time period during which the judgment of the condition of the converter
should take place
4) determining a frequency that provokes saturation of the catalytic converter when operating
with a lean or rich component during the judgment time period
5) calculating an average value of a maximum amount of the lean or rich component of the
exhaust gas absorbed in the catalytic converter by dividing a maximum value, obtained by
subtracting a total amount of the lean or rich component downstream of the catalytic
converter from a total amount of the lean or rich component upstream of the catalytic
converter during the judgment time period, with the saturation frequency of step 4
6) assessing the deterioration of the catalytic converter based on the average value of
maximum amount of the lean or rich component that is absorbed by the converter
The patent disclosure also describes methods to assess the deterioration of the upstream and
downstream oxygen sensors.
- e
NF J.-'----- rich I '
I
I
I area of lean I areaofrich
component I component b)
Integrated i /
areas of rich y//////A I I
and lean
//
component W/L timet
Fig. 98 (from DE19646008)