Page 266 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 266
248 Methods for Monitoring and Diagnosing the Eficiency of Catalytic Converters
c) the concentration of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gases entering the catalytic
converter, or
d) a combination of the operation parameters described in a)-c)
3) measuring the variation of the exhaust gas temperature inside the catalytic converter in
space or in time from the normal condition to the new conditions imposed
4) determining the degree of deterioration of the catalytic converter based on the behavior of
the measured temperature variation.
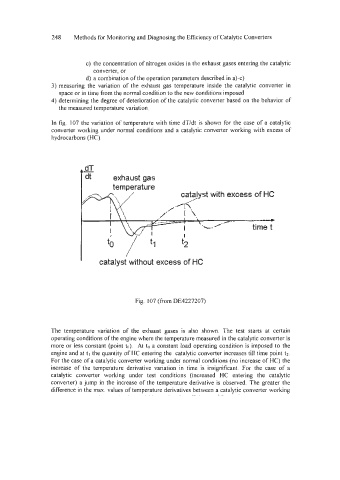
In fig. 107 the variation of temperature with time dT/dt is shown for the case of a catalytic
converter working under normal conditions and a catalytic converter working with excess of
hydrocarbons (HC).
-
dT
dt exhaust gas
temperature
catalyst with excess of HC
4
* ' * , I \* _.
'*<7
I
t
time
' I
/
catalyst without excess of HC
Fig. 107 (from DE4227207)
The temperature variation of the exhaust gases is also shown. The test starts at certain
operating conditions of the engine where the temperature measured in the catalytic converter is
more or less constant (point to). At to a constant load operating condition is imposed to the
engine and at tl the quantity of HC entering the catalytic converter increases till time point t2.
For the case of a catalytic converter working under normal conditions (no increase of HC) the
increase of the temperature derivative variation in time is insignificant. For the case of a
catalytic converter working under test conditions (increased HC entering the catalytic
converter) a jump in the increase of the temperature derivative is observed. The greater the
difference in the max. values of temperature derivatives between a catalytic converter working