Page 32 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 32
14 Methods for Monitoring and Diagnosing the Eficiency of Catalytic Converters
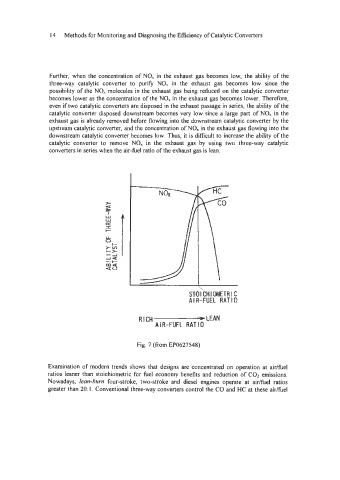
Further, when the concentration of NO, in the exhaust gas becomes low, the ability of the
three-way catalytic converter to purifl NO, in the exhaust gas becomes low since the
possibility of the NO, molecules in the exhaust gas being reduced on the catalytic converter
becomes lower as the concentration of the NO, in the exhaust gas becomes lower. Therefore,
even if two catalytic converters are disposed in the exhaust passage in series, the ability of the
catalytic converter disposed downstream becomes very low since a large part of NO, in the
exhaust gas is already removed before flowing into the downstream catalytic converter by the
upstream catalytic converter, and the concentration of NO, in the exhaust gas flowing into the
downstream catalytic converter becomes low. Thus, it is difficult to increase the ability of the
catalytic converter to remove NO, in the exhaust gas by using two three-way catalytic
converters in series when the air-he1 ratio of the exhaust gas is lean.
R I CH -
STO hi I DMETR I C
A I R-FUEL RAT I 0
A I R-FUEL RAT IO tEAN
Fig. 7 (from EP0627548)
Examination of modem trends shows that designs are concentrated on operation at aidfuel
ratios leaner than stoichiometric for fuel economy benefits and reduction of COz emissions.
Nowadays, lean-bum four-stroke, two-stroke and diesel engines operate at aidfuel ratios
greater than 20: 1. Conventional three-way converters control the CO and HC at these air/hel