Page 43 -
P. 43
32 2 Extremely Short-External-Cavity Laser Diode
In this chapter, we deal with LDs closely aligned with a microstructure
including a diaphragm, a cantilever and a slider. By closely aligning or inte-
grating the microstructure with an LD, which does not require a lens system,
new functional and sophisticated microdevices can be developed.
In the following, we analyze the ESEC LD by introducing the effective
reflectivity of the laser facet facingthe external mirror. Then a measurement
method that uses an LD attached to a flyingslider and a semitransparent
rotatingdisk mirror for an extremely short-external-cavity configuration is
presented. Then as practical applications, a tunable LD, a resonant sensor, an
integrated optically switched laser head are introduced from the viewpoint of
their composition, principle, basic characteristics, and fabrication methods.
2.2 Theoretical Analysis
The lasingbehavior for an ESEC LD with a feedback light has not yet been
clarified because of the complexity of the many parameters involved [2.9,
2.11]. In this section, we analyze the composite resonant phenomena under
the stronglight feedback. We first analyze a solitary LD and then an ESEC
LD by introducingthe effective reflectivity facet facingthe external mirror.
2.2.1 Lasing Condition of a Solitary LD
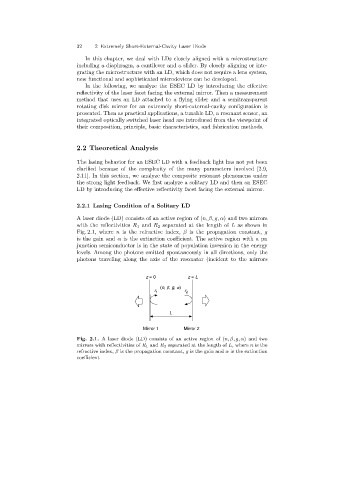
A laser diode (LD) consists of an active region of (n, β, g, α) and two mirrors
with the reflectivities R 1 and R 2 separated at the length of L as shown in
Fig. 2.1, where n is the refractive index, β is the propagation constant, g
is the gain and α is the extinction coefficient. The active region with a pn
junction semiconductor is in the state of population inversion in the energy
levels. Amongthe photons emitted spontaneously in all directions, only the
photons travelingalongthe axis of the resonator (incident to the mirrors
z = 0 z = L
(n, b, g, a)
r 1 r 2
L
Mirror 1 Mirror 2
Fig. 2.1. A laser diode (LD)consists of an active region of (n, β, g, α)and two
mirrors with reflectivities of R 1 and R 2 separated at the length of L,where n is the
refractive index, β is the propagation constant, g is the gain and α is the extinction
coefficient