Page 79 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 79
Computer Components 55
heating the spot with a laser allows the field to be changed and the drive
to be written.
All of these storage media have very different physical mechanisms
for storing information. Shared bus standards and hardware device
drivers allow the chipset to interact with them without needing the
details of their operation, and the chipset allows the processor to be
oblivious to even the bus standards being used.
Expansion Cards
To allow computers to be customized more easily, almost all mother-
boards include expansion slots that allow new circuit boards to be
plugged directly into the motherboard. These expansion cards provide
higher performance than features already built into the motherboard,
or add entirely new functionality. The connection from the expansion
cards to the chipset is called the expansion bus or sometimes the
input/output (I/O) bus.
In the original IBM PC, all communication internal to the system
box occurred over the expansion bus that was connected directly to the
processor and memory, and ran at the same clock frequency as the
processor. There were no separate processor, memory, or graphics buses.
In these systems, the expansion bus was simply “The Bus,” and the
original design was called Industry Standard Architecture (ISA). Some
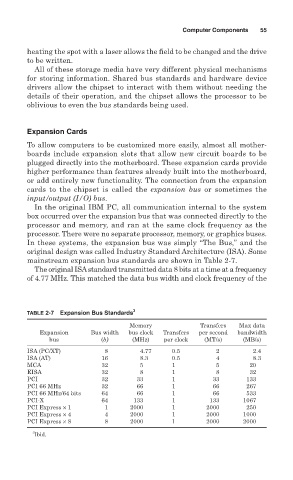
mainstream expansion bus standards are shown in Table 2-7.
The original ISAstandard transmitted data 8 bits at a time at a frequency
of 4.77 MHz. This matched the data bus width and clock frequency of the
3
TABLE 2-7 Expansion Bus Standards
Memory Transfers Max data
Expansion Bus width bus clock Transfers per second bandwidth
bus (b) (MHz) per clock (MT/s) (MB/s)
ISA (PC/XT) 8 4.77 0.5 2 2.4
ISA (AT) 16 8.3 0.5 4 8.3
MCA 32 5 1 5 20
EISA 32 8 1 8 32
PCI 32 33 1 33 133
PCI 66 MHz 32 66 1 66 267
PCI 66 MHz/64 bits 64 66 1 66 533
PCI-X 64 133 1 133 1067
PCI Express × 1 1 2000 1 2000 250
PCI Express × 4 4 2000 1 2000 1000
PCI Express × 8 8 2000 1 2000 2000
3
Ibid.