Page 77 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 77
Computer Components 53
for systems that are mainly used for 2D applications, the graphics
provided by these integrated solutions is often more than sufficient,
and the cost savings are significant.
Storage Devices
Because hard drives are universally used by computers as primary stor-
age, Southbridge chips of most chipsets have a bus specifically intended
for use with hard drives. Hard drives store binary data as magnetic dots
on metal platters that are spun at high speeds to allow the drive head
to read or to change the magnetic orientation of the dots passing beneath.
Hard drives have their own version of Moore’s law based not on shrink-
ing transistors but on shrinking the size of the magnetic dots used to store
data. Incredibly they have maintained the same kind of exponential
trend of increasing densities over the same time period using funda-
mentally different technologies from computer chip manufacturing. By
steadily decreasing the area required for a single magnetic dot, the hard
drive industry has provided steadily more capacity at lower cost. This
trend of rapidly increasing storage capacity has been critical in making
use of the rapidly increasing processing capacity of microprocessors.
More tightly packed data and higher spin rates have also increased the
maximum data transfer bandwidth drives support. This has created the
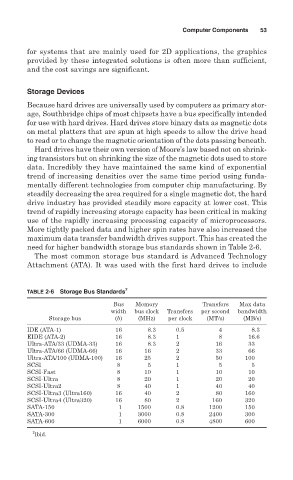
need for higher bandwidth storage bus standards shown in Table 2-6.
The most common storage bus standard is Advanced Technology
Attachment (ATA). It was used with the first hard drives to include
TABLE 2-6 Storage Bus Standards 2
Bus Memory Transfers Max data
width bus clock Transfers per second bandwidth
Storage bus (b) (MHz) per clock (MT/s) (MB/s)
IDE (ATA-1) 16 8.3 0.5 4 8.3
EIDE (ATA-2) 16 8.3 1 8 16.6
Ultra-ATA/33 (UDMA-33) 16 8.3 2 16 33
Ultra-ATA/66 (UDMA-66) 16 16 2 33 66
Ultra-ATA/100 (UDMA-100) 16 25 2 50 100
SCSI 8 5 1 5 5
SCSI-Fast 8 10 1 10 10
SCSI-Ultra 8 20 1 20 20
SCSI-Ultra2 8 40 1 40 40
SCSI-Ultra3 (Ultra160) 16 40 2 80 160
SCSI-Ultra4 (Ultra320) 16 80 2 160 320
SATA-150 1 1500 0.8 1200 150
SATA-300 1 3000 0.8 2400 300
SATA-600 1 6000 0.8 4800 600
2
Ibid.