Page 494 - Microsoft Office Excel 2003 Programming Inside Out
P. 494
Microsoft Office Excel 2003 Programming Inside Out
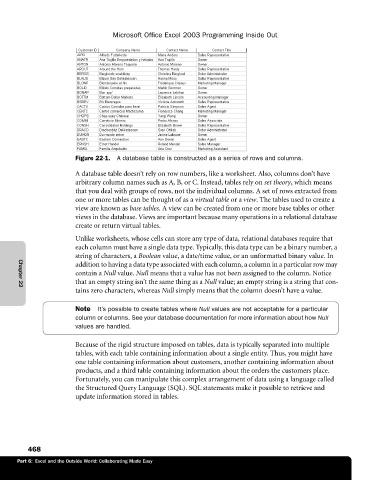
Figure 22-1. A database table is constructed as a series of rows and columns.
A database table doesn’t rely on row numbers, like a worksheet. Also, columns don’t have
arbitrary column names such as A, B, or C. Instead, tables rely on set theory, which means
that you deal with groups of rows, not the individual columns. A set of rows extracted from
one or more tables can be thought of as a virtual table or a view. The tables used to create a
view are known as base tables. A view can be created from one or more base tables or other
views in the database. Views are important because many operations in a relational database
create or return virtual tables.
Unlike worksheets, whose cells can store any type of data, relational databases require that
each column must have a single data type. Typically, this data type can be a binary number, a
string of characters, a Boolean value, a date/time value, or an unformatted binary value. In
addition to having a data type associated with each column, a column in a particular row may
contain a Null value. Null means that a value has not been assigned to the column. Notice
that an empty string isn’t the same thing as a Null value; an empty string is a string that con
tains zero characters, whereas Null simply means that the column doesn’t have a value.
Chapter 22
Note It’s possible to create tables where Null values are not acceptable for a particular
column or columns. See your database documentation for more information about how Null
values are handled.
Because of the rigid structure imposed on tables, data is typically separated into multiple
tables, with each table containing information about a single entity. Thus, you might have
one table containing information about customers, another containing information about
products, and a third table containing information about the orders the customers place.
Fortunately, you can manipulate this complex arrangement of data using a language called
the Structured Query Language (SQL). SQL statements make it possible to retrieve and
update information stored in tables.
468
Part 6: Excel and the Outside World: Collaborating Made Easy