Page 233 - MODELING OF ASPHALT CONCRETE
P. 233
Unified Disturbed State Constitutive Modeling of Asphalt Concr ete 211
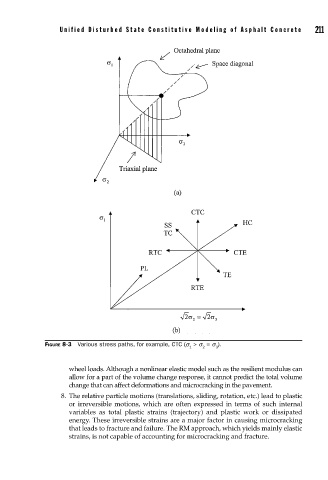
FIGURE 8-3 Various stress paths, for example, CTC (s > s = s ).
1 2 3
wheel loads. Although a nonlinear elastic model such as the resilient modulus can
allow for a part of the volume change response, it cannot predict the total volume
change that can affect deformations and microcracking in the pavement.
8. The relative particle motions (translations, sliding, rotation, etc.) lead to plastic
or irreversible motions, which are often expressed in terms of such internal
variables as total plastic strains (trajectory) and plastic work or dissipated
energy. These irreversible strains are a major factor in causing microcracking
that leads to fracture and failure. The RM approach, which yields mainly elastic
strains, is not capable of accounting for microcracking and fracture.