Page 76 - MODELING OF ASPHALT CONCRETE
P. 76
54 Cha pte r T w o
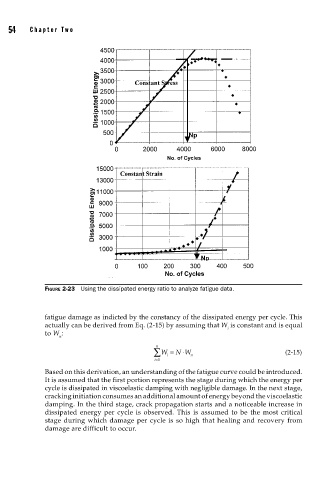
FIGURE 2-23 Using the dissipated energy ratio to analyze fatigue data.
fatigue damage as indicted by the constancy of the dissipated energy per cycle. This
actually can be derived from Eq. (2-15) by assuming that W is constant and is equal
i
to W :
n
n
⋅
∑ W = N W n (2-15)
i
i=1
Based on this derivation, an understanding of the fatigue curve could be introduced.
It is assumed that the first portion represents the stage during which the energy per
cycle is dissipated in viscoelastic damping with negligible damage. In the next stage,
cracking initiation consumes an additional amount of energy beyond the viscoelastic
damping. In the third stage, crack propagation starts and a noticeable increase in
dissipated energy per cycle is observed. This is assumed to be the most critical
stage during which damage per cycle is so high that healing and recovery from
damage are difficult to occur.