Page 293 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 293
Introduction to Reactor Design Fundamentals for Ideal Systems 263
Information on the composition and temperature changes is obtained
from the rate equation, while the mixing patterns are related to the
intensity of mixing and reactor geometry. Heat transfer is referred to
as the exothermic or endothermic nature of the reactions and the mass
transfer to the heterogeneous systems.
GENERAL MASS BALANCE
For the ideal reactors considered, the design equations are based
on the mass conservation equations. With this in mind, a suitable
component is chosen (i.e., reactant or product). Consider an element
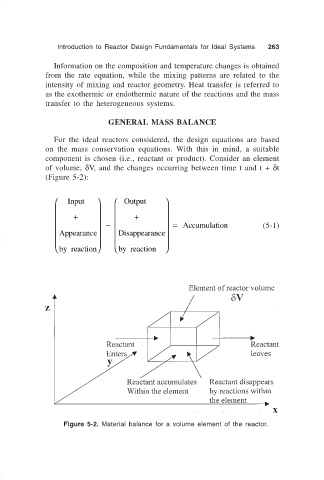
of volume, δV, and the changes occurring between time t and t + δt
(Figure 5-2):
Input Output
+ +
− = Accumulation (5-1)
Appearance Disappearance
by reaction by reaction
Figure 5-2. Material balance for a volume element of the reactor.