Page 275 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 275
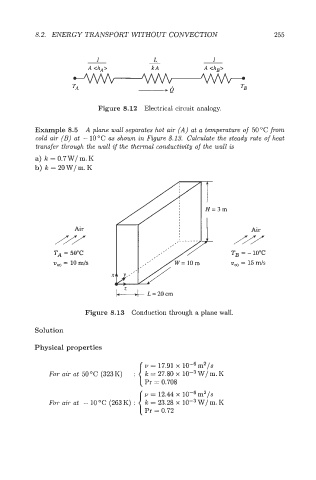
8.2. ENERGY TRANSPORT WTHOUT CONVECTION 255
L
1 - 1
A <hA> kA A <hB>
-Q
Figure 8.12 Electrical circuit analogy.
Example 8.5 A plane wall separates hot air (A) at a temperature of 5OoC from
cold air (B) at - 10°C as shown in Figure 8.13. Calculate the steady rate of heat
transfer through the wall if the thermal conductivity of the wall is
a) k = 0.7 W/ m. K
b) IC = 20W/m.K
3m
Air Air
/// ///
TA = 50°C Tg = - 10°C
urn = 10 m/s vq, = 15 4 s
~=20cm
Figure 8.13 Conduction through a plane wall.
Solution
Physical properties
Y = 17.91 x 10-6m2/s
For air at 50 "C (323 K) k = 27.80 x W/ m. K
Pr = 0.708
v = 12.44 x m2/s
For air at - 10°C (263K) k = 23.28 x W/m. K
Pr = 0.72