Page 289 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 289
8.2. ENERGY TRANSPORT WTHOUT CONVECTION 269
c) The dominant resistance to heat transfer is the resistance of fluid B. Hence, the
overall heat transfer coefficients are
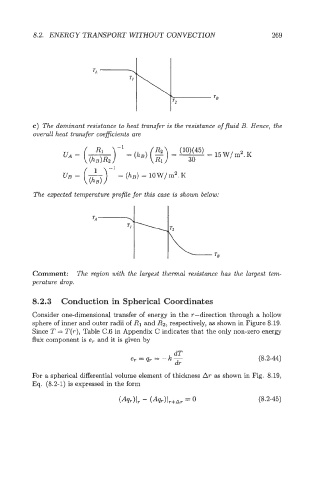
The expected temperature profile for this case is shown below:
Comment: The region with the largest thermal resistance has the largest tem-
perature drop.
8.2.3 Conduction in Spherical Coordinates
Consider one-dimensional transfer of energy in the r-direction through a hollow
sphere of inner and outer radii of R1 and R2, respectively, as shown in Figure 8.19.
Since T = T(r), Table C.6 in Appendix C indicates that the only non-zero energy
flui component is e, and it is given by
dT
e, = q, = - k - (8.2-44)
dr
For a spherical differential volume element of thickness Ar BS shown in Fig. 8.19,
Eq. (8.2-1) is expressed in the form