Page 47 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 47
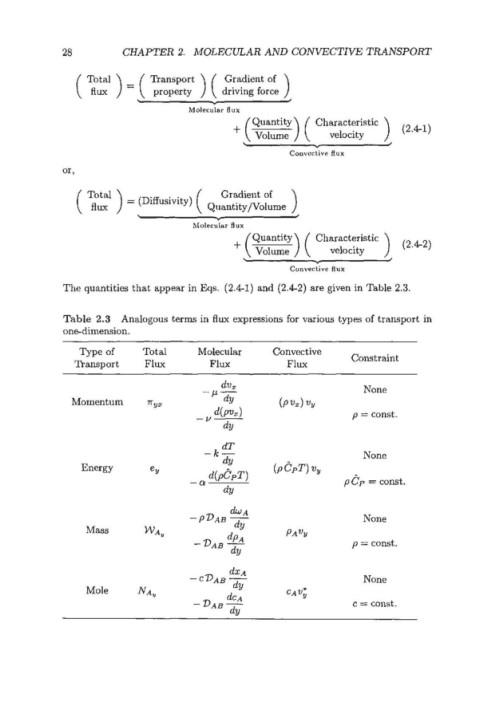
28 CHAPTER 2. MOLECULAR AND CONVECTIVE TRANSPORT
Transport ) ( Gradient of )
property driving force
L -c 4
Molecular flux
+[ Volume ) ( Characteristic
Quantity
velocity
* d
Convective flux
( ) = (Diffusivity) ( Q::z$::me
2:'
L
Molecular flux
+ ( Volume ) ( Characteristic
Quantity
velocity
Convective flux
The quantities that appear in Eqs. (2.4-1) and (2.4-2) are given in Table 2.3.
Table 2.3 Analogous terms in flux expressions for various types of transport in
onedimension.
Type of Total Molecular Convective Constraint
Transport Flux Flux Flux
dvx None
-P-
Momentum rYZ dY (P vx) VY
d(P4 p = const.
-u-
dY
Energy eY
&A
-P~AB - None
Mass WA, d!l PA%
dpA
-DAB - p = const.
dY