Page 33 - Modern Analytical Chemistry
P. 33
1400-CH02 9/8/99 3:48 PM Page 16
16 Modern Analytical Chemistry
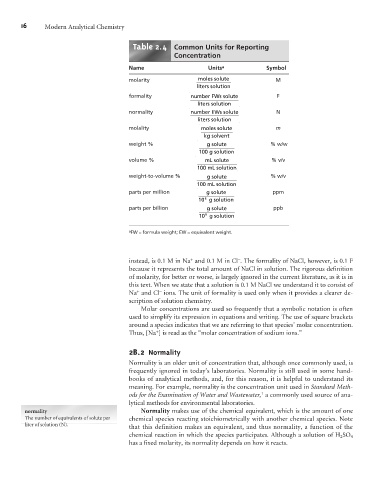
Table 2.4 Common Units for Reporting
Concentration
Name Units a Symbol
molarity moles solute M
liters solution
formality number F Ws solute F
liters solution
normality number E Ws solute N
liters solution
molality moles solute m
g
k solvent
weight % g solute % w/w
100 g solution
volume % m solute % v/v
L
100 mL solution
weight-to-volume % g solute % w/v
100 mL solution
parts per million g solute ppm
10 6 g solution
parts per billion g solute ppb
g solution
10 9
a FW =formula weight; EW =equivalent weight.
+
–
instead, is 0.1 M in Na and 0.1 M in Cl . The formality of NaCl, however, is 0.1 F
because it represents the total amount of NaCl in solution. The rigorous definition
of molarity, for better or worse, is largely ignored in the current literature, as it is in
this text. When we state that a solution is 0.1 M NaCl we understand it to consist of
+
–
Na and Cl ions. The unit of formality is used only when it provides a clearer de-
scription of solution chemistry.
Molar concentrations are used so frequently that a symbolic notation is often
used to simplify its expression in equations and writing. The use of square brackets
around a species indicates that we are referring to that species’ molar concentration.
+
Thus, [Na ] is read as the “molar concentration of sodium ions.”
2B.2 Normality
Normality is an older unit of concentration that, although once commonly used, is
frequently ignored in today’s laboratories. Normality is still used in some hand-
books of analytical methods, and, for this reason, it is helpful to understand its
meaning. For example, normality is the concentration unit used in Standard Meth-
1
ods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, a commonly used source of ana-
lytical methods for environmental laboratories.
normality Normality makes use of the chemical equivalent, which is the amount of one
The number of equivalents of solute per chemical species reacting stoichiometrically with another chemical species. Note
liter of solution (N).
that this definition makes an equivalent, and thus normality, a function of the
chemical reaction in which the species participates. Although a solution of H 2 SO 4
has a fixed molarity, its normality depends on how it reacts.