Page 38 - Modern Control Systems
P. 38
Chapter 1 Introduction to Control Systems
Machines that automatically load and unload, cut, weld, or cast are used by industry
to obtain accuracy, safety, economy, and productivity [14,27,28,38]. The use of com-
puters integrated with machines that perform tasks like a human worker has been
foreseen by several authors. In his famous 1923 play, entitled R.U.R. [48], Karel
Capek called artificial workers robots, deriving the word from the Czech noun
roboia, meaning "work."
A robot is a computer-controlled machine and involves technology closely asso-
ciated with automation. Industrial robotics can be defined as a particular field of
automation in which the automated machine (that is, the robot) is designed to sub-
stitute for human labor [18, 27, 33]. Thus robots possess certain humanlike charac-
teristics. Today, the most common humanlike characteristic is a mechanical
manipulator that is patterned somewhat after the human arm and wrist. Some de-
vices even have anthropomorphic mechanisms, including what we might recognize
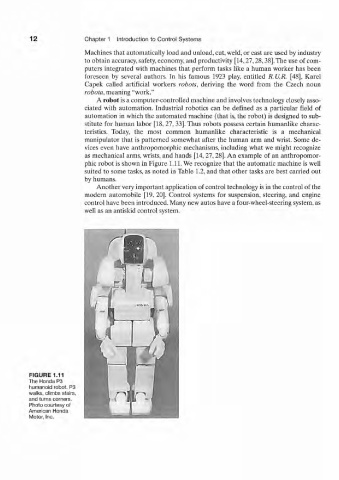
as mechanical arms, wrists, and hands [14, 27,28]. An example of an anthropomor-
phic robot is shown in Figure 1.11. We recognize that the automatic machine is well
suited to some tasks, as noted in Table 1.2, and that other tasks are best carried out
by humans.
Another very important application of control technology is in the control of the
modern automobile [19, 20]. Control systems for suspension, steering, and engine
control have been introduced. Many new autos have a four-wheel-steering system, as
well as an antiskid control system.
FIGURE 1.11
The Honda P3
humanoid robot. P3
walks, climbs stairs,
and turns corners.
Photo courtesy of
American Honda
Motor, Inc.