Page 263 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 263
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 123
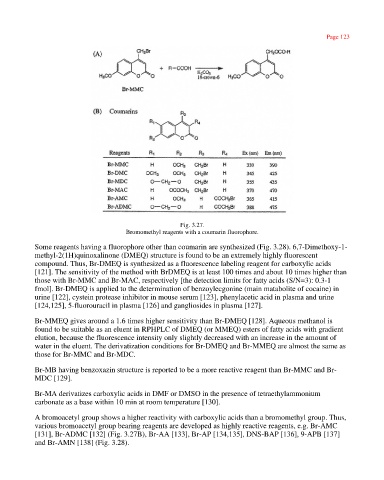
Fig. 3.27.
Bromomethyl reagents with a coumarin fluorophore.
Some reagents having a fluorophore other than coumarin are synthesized (Fig. 3.28). 6,7-Dimethoxy-1-
methyl-2(1H)quinoxalinone (DMEQ) structure is found to be an extremely highly fluorescent
compound. Thus, Br-DMEQ is synthesized as a fluorescence labeling reagent for carboxylic acids
[121]. The sensitivity of the method with BrDMEQ is at least 100 times and about 10 times higher than
those with Br-MMC and Br-MAC, respectively [the detection limits for fatty acids (S/N=3): 0.3-1
fmol]. Br-DMEQ is applied to the determination of benzoylecgonine (main matabolite of cocaine) in
urine [122], cystein protease inhibitor in mouse serum [123], phenylacetic acid in plasma and urine
[124,125], 5-fluorouracil in plasma [126] and gangliosides in plasma [127].
Br-MMEQ gives around a 1.6 times higher sensitivity than Br-DMEQ [128]. Aqueous methanol is
found to be suitable as an eluent in RPHPLC of DMEQ (or MMEQ) esters of fatty acids with gradient
elution, because the fluorescence intensity only slightly decreased with an increase in the amount of
water in the eluent. The derivatization conditions for Br-DMEQ and Br-MMEQ are almost the same as
those for Br-MMC and Br-MDC.
Br-MB having benzoxazin structure is reported to be a more reactive reagent than Br-MMC and Br-
MDC [129].
Br-MA derivatizes carboxylic acids in DMF or DMSO in the presence of tetraethylammonium
carbonate as a base within 10 min at room temperature [130].
A bromoacetyl group shows a higher reactivity with carboxylic acids than a bromomethyl group. Thus,
various bromoacetyl group bearing reagents are developed as highly reactive reagents, e.g. Br-AMC
[131], Br-ADMC [132] (Fig. 3.27B), Br-AA [133], Br-AP [134,135], DNS-BAP [136], 9-APB [137]
and Br-AMN [138] (Fig. 3.28).
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_123.ht... 30/09/2003