Page 74 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 74
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 27
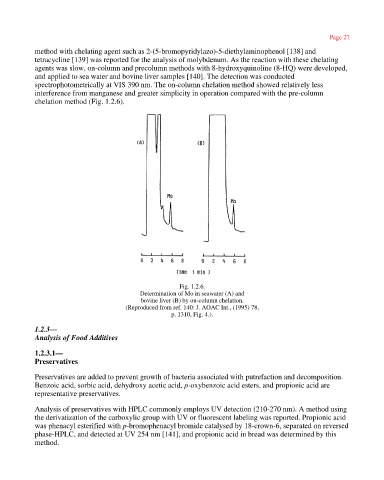
method with chelating agent such as 2-(5-bromopyridylazo)-5-diethylaminophenol [138] and
tetracycline [139] was reported for the analysis of molybdenum. As the reaction with these chelating
agents was slow, on-column and precolumn methods with 8-hydroxyquinoline (8-HQ) were developed,
and applied to sea water and bovine liver samples [140]. The detection was conducted
spectrophotometrically at VIS 390 nm. The on-column chelation method showed relatively less
interference from manganese and greater simplicity in operation compared with the pre-column
chelation method (Fig. 1.2.6).
Fig. 1.2.6.
Determination of Mo in seawater (A) and
bovine liver (B) by on-column chelation.
(Reproduced from ref. 140: J. AOAC Int., (1995) 78,
p. 1310, Fig. 4.).
1.2.3—
Analysis of Food Additives
1.2.3.1—
Preservatives
Preservatives are added to prevent growth of bacteria associated with putrefaction and decomposition.
Benzoic acid, sorbic acid, dehydroxy acetic acid, p-oxybenzoic acid esters, and propionic acid are
representative preservatives.
Analysis of preservatives with HPLC commonly employs UV detection (210-270 nm). A method using
the derivatization of the carboxylic group with UV or fluorescent labeling was reported. Propionic acid
was phenacyl esterified with p-bromophenacyl bromide catalysed by 18-crown-6, separated on reversed
phase-HPLC, and detected at UV 254 nm [141], and propionic acid in bread was determined by this
method.
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_27.html 30/09/2003