Page 256 - MODERN ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 256
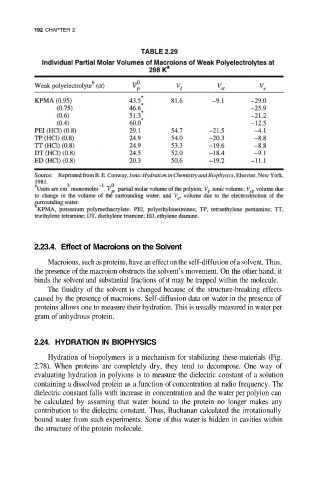
192 CHAPTER 2
2.23.4. Effect of Macroions on the Solvent
Macroions, such as proteins, have an effect on the self-diffusion of a solvent. Thus,
the presence of the macroion obstructs the solvent’s movement. On the other hand, it
binds the solvent and substantial fractions of it may be trapped within the molecule.
The fluidity of the solvent is changed because of the structure-breaking effects
caused by the presence of macroions. Self-diffusion data on water in the presence of
proteins allows one to measure their hydration. This is usually measured in water per
gram of anhydrous protein.
2.24. HYDRATION IN BIOPHYSICS
Hydration of biopolymers is a mechanism for stabilizing these materials (Fig.
2.78). When proteins are completely dry, they tend to decompose. One way of
evaluating hydration in polyions is to measure the dielectric constant of a solution
containing a dissolved protein as a function of concentration at radio frequency. The
dielectric constant falls with increase in concentration and the water per polyion can
be calculated by assuming that water bound to the protein no longer makes any
contribution to the dielectric constant. Thus, Buchanan calculated the irrotationally
bound water from such experiments. Some of this water is hidden in cavities within
the structure of the protein molecule.