Page 93 - MODERN ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 93
36 CHAPTER 2
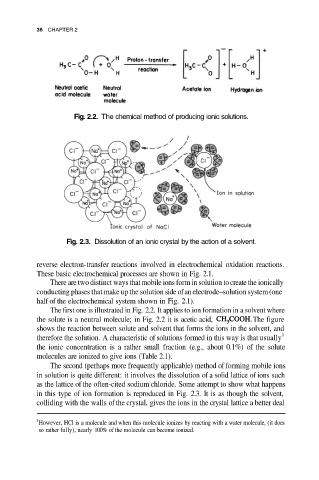
Fig. 2.2. The chemical method of producing ionic solutions.
Fig. 2.3. Dissolution of an ionic crystal by the action of a solvent.
reverse electron-transfer reactions involved in electrochemical oxidation reactions.
These basic electrochemical processes are shown in Fig. 2.1.
There are two distinct ways that mobile ions form in solution to create the ionically
conducting phases that make up the solution side of an electrode–solution system (one
half of the electrochemical system shown in Fig. 2.1).
The first one is illustrated in Fig. 2.2. It applies to ion formation in a solvent where
the solute is a neutral molecule; in Fig. 2.2 it is acetic acid, The figure
shows the reaction between solute and solvent that forms the ions in the solvent, and
1
therefore the solution. A characteristic of solutions formed in this way is that usually
the ionic concentration is a rather small fraction (e.g., about 0.1%) of the solute
molecules are ionized to give ions (Table 2.1).
The second (perhaps more frequently applicable) method of forming mobile ions
in solution is quite different: it involves the dissolution of a solid lattice of ions such
as the lattice of the often-cited sodium chloride. Some attempt to show what happens
in this type of ion formation is reproduced in Fig. 2.3. It is as though the solvent,
colliding with the walls of the crystal, gives the ions in the crystal lattice a better deal
1
However, HCl is a molecule and when this molecule ionizes by reacting with a water molecule, (it does
so rather fully), nearly 100% of the molecule can become ionized.