Page 162 - Modern Optical Engineering The Design of Optical Systems
P. 162
Prism and Mirror Systems 145
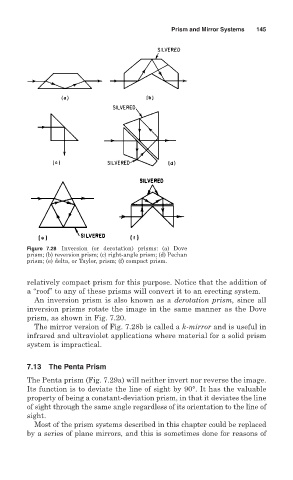
Figure 7.28 Inversion (or derotation) prisms: (a) Dove
prism; (b) reversion prism; (c) right-angle prism; (d) Pechan
prism; (e) delta, or Taylor, prism; (f) compact prism.
relatively compact prism for this purpose. Notice that the addition of
a “roof” to any of these prisms will convert it to an erecting system.
An inversion prism is also known as a derotation prism, since all
inversion prisms rotate the image in the same manner as the Dove
prism, as shown in Fig. 7.20.
The mirror version of Fig. 7.28b is called a k-mirror and is useful in
infrared and ultraviolet applications where material for a solid prism
system is impractical.
7.13 The Penta Prism
The Penta prism (Fig. 7.29a) will neither invert nor reverse the image.
Its function is to deviate the line of sight by 90°. It has the valuable
property of being a constant-deviation prism, in that it deviates the line
of sight through the same angle regardless of its orientation to the line of
sight.
Most of the prism systems described in this chapter could be replaced
by a series of plane mirrors, and this is sometimes done for reasons of