Page 247 - Modern Optical Engineering The Design of Optical Systems
P. 247
Optical Materials 227
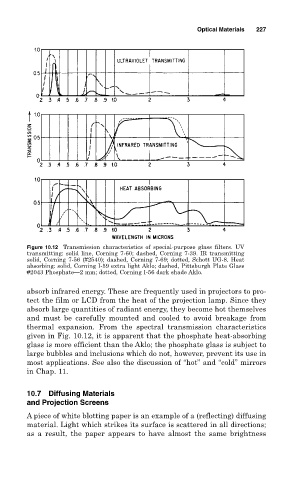
Figure 10.12 Transmission characteristics of special-purpose glass filters. UV
transmitting: solid line, Corning 7-60; dashed, Corning 7-39. IR transmitting
solid, Corning 7-56 (#2540); dashed, Corning 7-69; dotted, Schott UG-8. Heat
absorbing: solid, Corning I-59 extra light Aklo; dashed, Pittsburgh Plate Glass
#2043 Phosphate—2 mm; dotted, Corning I-56 dark shade Aklo.
absorb infrared energy. These are frequently used in projectors to pro-
tect the film or LCD from the heat of the projection lamp. Since they
absorb large quantities of radiant energy, they become hot themselves
and must be carefully mounted and cooled to avoid breakage from
thermal expansion. From the spectral transmission characteristics
given in Fig. 10.12, it is apparent that the phosphate heat-absorbing
glass is more efficient than the Aklo; the phosphate glass is subject to
large bubbles and inclusions which do not, however, prevent its use in
most applications. See also the discussion of “hot” and “cold” mirrors
in Chap. 11.
10.7 Diffusing Materials
and Projection Screens
A piece of white blotting paper is an example of a (reflecting) diffusing
material. Light which strikes its surface is scattered in all directions;
as a result, the paper appears to have almost the same brightness